UNRC – FCEFQN – DPTO GEOLOGÍA INTRODUCCIÓN A LOS
UNRC – FCEFQN – DPTO GEOLOGÍA INTRODUCCIÓN A LOS
Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto
UNRC – FCEFQN – Dpto. GEOLOGÍA- Introducción a los SIG - 2019
|
Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físico – Químicas y Naturales |
||||||
|
DEPARTAMENTO |
GEOLOGÍA |
CARRERA |
Licenciatura en Geología |
|||
|
ASIGNATURA |
INTRODUCCIÓN A LOS SISTEMAS DE INFORMACIÓN GEOGRÁFICA |
CÓDIGO |
3650 |
|||
|
Profesores Responsables |
Osvaldo CAMPANELLA
|
AÑO ACADÉMICO |
2021 |
|||
|
Colaboradores |
|
Orientación |
Optativa. Formación complementaria |
|||
|
Régimen |
CUATRIMESTRAL – 2º CUATRIMESTRE |
|||||
|
Requisitos para regularizar |
Aprobación del 80% de las clases. Aprobación de una única evaluación de integración escrita con un recuperatorio. Se aprueba el examen con el 60%. |
|||||
|
Requisitos para promocionar |
No se prevee régimen de promoción |
|||||
|
Asignación de horas semanales |
Una clase TP semanales de 4 hs. Cuatrimestral. |
|||||
|
Exámenes parciales |
Un examen escrito al final de la asignatura con un recuperatorio. |
|||||
|
Examen final |
Evaluación oral de conocimientos generales. |
|||||
I.1 OBJETIVOS GENERALES
Introducir al estudiante en la tecnología de los Sistemas de Información Geográfica (SIG)
I.1 OBJETIVOS ESPECÍFICOS
Introducir al estudiante en las potencialidades de los SIG.
Introducir al estudiante en las opciones de programas de aplicación disponibles.
Capacitar al estudiante en la forma de organización de los datos y la información dentro de un proyecto SIG.
Introducir al estudiante en el diseño de bases de datos aptas para los SIG.
Introducir al estudiante en las potencialidades el análisis espacial.
II CONTENIDOS DE APRENDIZAJE
|
TEMA |
CONTENIDO |
|
1 |
Ejemplos de proyectos SIG sobre la aplicación QGIS. |
|
2 |
Organización de la información: Proyecto, Vista, Tabla, Salida, Rutinas. |
|
3 |
Componentes básicos de una aplicación SIG. Distintos programas disponibles: Libres y gratuitos y pagos. |
|
4 |
El espacio vectorial vs el espacio raster. |
|
5 |
Datos abiertos. Accesibilidad a los datos |
|
5 |
Introducción a las Bases de Datos. Modelo Entidad Relación |
|
6 |
Introducción al Análisis Espacial. |
III FORMAS METODOLÓGICAS DE ENSEÑANZA Y APRENDIZAJE
La premisa fundamental es la de introducir al estudiante en las tecnologías de los SIG. Se parte del supuesto de un conocimiento nulo y, luego de una aproximación analítica a las técnicas disponibles, se procurará un acercamiento integral mediante un “caso” de estudio.
IV GUIA DE ACTIVIDADES
Se actualiza en el desarrollo del proceso de enseñanza aprendizaje en función de los conocimientos y potencialidades de los estudiantes.
VI BIBLIOGRAFÍA
La presente lista es sólo de los principales libros y publicaciones. En la guía de actividades se entrega una lista más detallada de la bibliografía disponible. Se entregan, además, bibliografía en soporte digital.
Aronoff, S. 1995. Geographic Information Systems: A Management Perspective. WDL Publications, Ottawa, Canadá.
Brodie, R.S. 1998. Integrating Gis and RDBMS Technologies During Construction of a Regional Groundwater Model. Environmental Modelling and Software, 14(2-3): 119-128.
Chen, P. 1977. The Entity-Relationship Approach to Logical Data Base Design. In The Q.E.D. Monograph Series: Data Management. Edited by M. Wellesley, Vol.1, pp. 9 - 36.
Dai, F.C., Lee, C.F., and Zhang, X.H. 2001. Gis-Based Geo-Environmental Evaluation for Urban Land_Use Planning: A Case Study. Engineering Geology, 61: 257-271.
Dengsheng Lua, Q.W. 2006. Use of Impervious Surface in Urban Land-Use Classification. Remote Sensing and Environment, 102(1 2): 146 160.
Densham, F.C., Lee, C.F., and Zhang, X.H. 2001. Gis-Based Geo-Environmental Evaluation for Urban Land-Use Planning: A Case Study. Engineering Geology, 61: 257–271.
Diamond, J.T., and Wright, J.R. 1988. Design of an Integrated Spatial Information System for Multiobjective Land Use Planning. Environment and Planning, B 15(12): 205-214.
Esri 1998. Arcview Gis. The Geographic Information System for Everyone.
Esri 1999. Arcview Gis 3.2. Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc.
Gómez-Rubio, V., and López-Quílez, A. 2005. Rarcinfo: Using Gis Data with R. Computers & Geosciences, 31: 1000 - 1006.
Goodchild, M.F. 1993. The State of Gis for Environmetal Problem Solving. In Environmental Modelling with Gis. Oxford University Press, New York. pp. 8-15.
Jiang, H., and Eastman, J.R. 2000. Aplication of Fuzzy Measures in Multi-Criteria Evaluation in Gis. Internacional Journal of Geographical Information Systems, 14(2): 173-184.
Keller, C.P. 1996. Decision Making Using Multiple Criteria.
Lacan, I., Zhou, J.Y., Liu, K.-S., and Waldman, J. 2006. A Geographic Information Systems (Gis) and Spatial Modeling Approach to Assessing Indoor Radon Potential at Local Level. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 64: 490 - 496.
Lembo, A.J.J., Young Lew, M., Laba, M., and Baveye, P. 2006. Use of Spatial Sql to Assess the Practical Significance of the Modifiable Areal Unit Problem. Computers & Geosciences, 32(2): 270-274.
Malczewski, J. 1999. Gis and Multicriteria Decision Analysis. John Willey and Sons Inc.
Martin, D., Longley, P., and Higgs, G. 1994. The Use of Gis in the Analysis of Diverse Urban Databases. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 18(1): 55-66.
Mcconnell, L.M., Van Vliet, D., and Cook, T.J. 2006. A New Suite of User-Friendly Gis Tools for Accessing Environmental Monitoring Databases. In 2006 ESRI User Conference. Edited by ESRI.
Mundia, C.N., and Aniya, M. 2005. Analysis of Land Use/Cover Changes and Urban Expansion of Nairobi City Using Remote Sensing and Gis. International-Journal-of-Remote-Sensing, 26 (13): 2831-2849.
NASA. 2008. The Remote Sensing Tutorial. http://rst.gsfc.nasa.gov/
Passmore, J. 1997. Construction of a Dynamic Gis Tool Kit for the Visualization, Analysis and Prediction of Bankline Movement Along the Jamuna River, Bangladesh, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham.
Reitner, H., and Lipiarski, P. 1994. Wellmaster - Processing of Borehole-Data with Arcinfo and Arcview. In 13º European ESRI User Conference. Edited by ESRI. Firenze, Italy. ESRI.
Tait, N.G., Davison, R.M., Whittaker, J.J., Leharne, S.A., and Lerner, D.N. 2004. Borehole Optimisation System (Bos) a Gis Based Risk Analysis Tool for Optimising the Use of Urban Groundwater. Environmental Modelling & Software, 19: 1111 1124.
Thome, K., Palluconi, F., Takashima, T., and Masuda, K. 1998. Atmospheric Correction of Aster. IEEE Transactions of Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 36(4): 1199 - 1211.
Tags: fcefqn –, geología, introducción, fcefqn
- 11 OPĆINA JARMINA NA TEMELJU ODREDBE ČLANKA 32 STAVKA
- PODER LEGISLATIVO LEY Nº 301 QUE CONCEDE PENSION GRACIABLE
- FECHA DE VIGENCIA NÚMERO DE REVISIÓN NORMA DE REFERENCIA
- “ INSIDE US ” GUIÓN JAVIER PALOMINO SEC 1
- LA FAMILIA DE PRODUCTOS DEPORTIVOS AL COMPLETO EL
- PONTIFICIA UNIVERSIDAD JAVERIANA JUAN GABRIEL OSUNA – DIANA ARÉVALO
- REPORT NUMBER EV90342 PAGE 25 OF 25 THERMAL IMPEDANCE
- PROGRAMIRANJE 1 2 KOLOKVIJ IME IN PRIIMEK (ČAS
- 11 PLANEACIÓN EN LA UNIVERSIDAD JAVERIANA SEDE DE BOGOTÁ
- PLEASE COMPLETE ALL SECTIONS OF THIS FORM DISTRICTSUPREME COURT
- LAMPIRAN 1 SILABUS MATA KULIAH PENDIDIKAN AGAMA BOBOT
- NUEVOS DESAFÍOS DE LA TEORÍA DE GOVERNANCE POR RENATE
- EXPERIMENTAL SUBJECT’S BILL OF RIGHTS – MEDICAL RESEARCH CALIFORNIA
- 2 GUIDO RINGS GUIDO RINGS PRESENTACIÓN DURANTE LA GUERRA
- LA MUSICA DEL TARDO ROMANTICISMO (DA PAG 188 A
- NAME LAB SECTION CPRE 288 FALL 2021 – HOMEWORK
- DNIA (MIEJSCOWOŚĆ DATA) PREZYDENT MIASTA ZAWIERCIE UL
- LR 9 AGOSTO 1999 N° 22 C ONSIGLIO REGIONALE
- WASHINGTON STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH ACCOUNTING AND REPORTING MANUAL
- AKTUALISASI KURIKULUM 2013 DI SEKOLAH DASAR MELALUI GERAKAN LITERASI
- INSIDE OUT THANKSGIVING DAY WORKSHEET A 1 MATCH
- DIARI D’UNA TURISTA 13 DE NOVEMBRE 1700H AVUI HE
- VEILEDNING I FORHOLD TIL LEGEMIDDELHÅNDTERING I SKOLESFOBARNEHAGE 1 FORMÅL
- EXCMA DIPUTACIÓN PROVINCIAL GUADALAJARA TESORERÍA ALVO REFINANCIACIÓN DE CUATRO
- LAKIP PENGADILAN NEGERI KENDAL TAHUN 2015 BAB I
- PROGRAM POTWIERDZANIA KWALIFIKACJI OSÓB PRACUJĄCYCH W OBSZARZE PROFILAKTYKI I
- INSTITUTIONAL REVIEW BOARD (IRB) GUIDELINES FOR SUBJECT ACCRUAL
- PROTEA GARDENS MARKETING CNR ALEKHINE & OLD POTCH
- MEETING THE EMPLOYMENT TRANSPORTATION NEEDS OF PEOPLE WITH DISABILITIES
- 85 М Н ВОРОБЬЕВА ФОРМИРОВАНИЕ И СОВЕРШЕНСТВОВАНИЕ НАВЫКОВ ПРОИЗНОШЕНИЯ
“c a t r a c h o” tel
 SEMEJANZA DE FIGURAS PLANAS DOS FIGURAS SON SEMEJANTES SI
SEMEJANZA DE FIGURAS PLANAS DOS FIGURAS SON SEMEJANTES SIPLANNING FOR A COLLEGE FAIR EARLY CONSIDERATION
 LEGAL VISITORS ACCESS TO IT IN THE ESTABLISHMENT IN
LEGAL VISITORS ACCESS TO IT IN THE ESTABLISHMENT IN PROCEDIMIENTO PARA LA EMISIÓN Y RECEPCIÓN DE OPINIONES DE
PROCEDIMIENTO PARA LA EMISIÓN Y RECEPCIÓN DE OPINIONES DE SUMMARY OF LOGO COMMANDS (MSW LOGO) THESE WILL GET
SUMMARY OF LOGO COMMANDS (MSW LOGO) THESE WILL GET SISTEMAS DE NUMERACIÓN 1 INTRODUCCIÓN CUANDO LOS HOMBRES EMPEZARON
SISTEMAS DE NUMERACIÓN 1 INTRODUCCIÓN CUANDO LOS HOMBRES EMPEZARONKONKURS PLASTYCZNY „SEGREGUJĘ – MAZURY RATUJE” DECYZJĄ GMINNYCH KOMISJI
 ESTADÍSTICA DESCRIPTIVA EN GEOGRAFÍA TITULACIÓN DE GEOGRAFÍA ASIGNATURA OBLIGATORIA
ESTADÍSTICA DESCRIPTIVA EN GEOGRAFÍA TITULACIÓN DE GEOGRAFÍA ASIGNATURA OBLIGATORIAFRA KRISTINA SAMUELSEN SENDT 16 NOVEMBER 2005 1312 TIL
CHAPTER 5 ACCOUNTING FOR MERCHANDISING BUSINESSES DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
 W WWEJERCICIOSDEFÍSICACOM EJERCICIOS PARA RESOLVER MRU Y MRUV MOVIMIENTO
W WWEJERCICIOSDEFÍSICACOM EJERCICIOS PARA RESOLVER MRU Y MRUV MOVIMIENTOAGREEMENT ESTABLISHING A FOOD AND FERTILISER TECHNOLOGY CENTRE FOR
HRVATSKI SAŽETAK OPISA SVOJSTAVA LIJEKA 64 POSEBNE MJERE
ABDOMINAL HYSTERECTOMY THE REMOVAL OF THE UTERUS WITH (TOTAL)
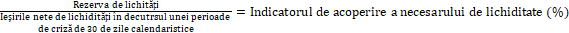 TABEL DE CONCORDANȚĂ 1 TITLUL ACTULUI UNIUNII EUROPENE INCLUSIV
TABEL DE CONCORDANȚĂ 1 TITLUL ACTULUI UNIUNII EUROPENE INCLUSIVDE DE 2006 DECRETO N° HUGO CHAVEZ FRIAS PRESIDENTE
ZAŁĄCZNIK NR 5 DO WNIOSKU O REFUNDACJĘ FORMULARZ OPERACJI
 NOMBRE DEL DOCUMENTO PROCEDIMIENTO DEL SGC PARA ATENCIÓN DE
NOMBRE DEL DOCUMENTO PROCEDIMIENTO DEL SGC PARA ATENCIÓN DEZAŁĄCZNIK 4 DO REGULAMINU KONKURSU METRYCZKA ZADANIA NAZWA I