FALLS RISK GUIDE RNLPN FALLS THE JOINT COMMISSION ON
SENECA FALLS NACIMIENTO DEL MOVIMIENTO ASOCIACIONISTA FEMENINOUNVERBINDLICHES MUSTER DAS UNTER BERÜCKSICHTIGUNG DES EINZELFALLS ANZUPASSEN
1 FALLSTUDIE ZUR ÜBUNG RECHNUNGSWESEN UND FINANZIERUNG AN DER
1040 EIGHTH AVENUE 2ND FLOOR BEAVER FALLS PA 15010
15A NCAC 02B 0279 FALLS WATER SUPPLY NUTRIENT STRATEGY
2(2) TRANSPORTDOKUMENT ENLIGT AVFALLSFÖRORDNINGEN 2001106341§ OCH NATURVÅRDSVERKETS FÖRESKRIFTER NFS

Falls Risk Guide
RN/LPN
Falls
The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) 2005 National Patient Safety Goals requires hospitals to assess and periodically reassess each patient's risk for falling. At Methodist Hospital the total number of reported falls in 2005 was 197 and it is increasing every year, Out of these 80 had reported injuries, 3 had root cause analysis (RCA) completed and 1 was a reportable event. Through RCA we identified that our current falls assessment tool did not accurately capture patients at risk for falls, therefore we had missed opportunities to prevent falls. Further more we did not have many visuals alerting staff that the patient is a falls risk and the visible interventions that correspond with that specific risk.
According to a study supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality , many falls in hospital happen when the patient is alone or involved in elimination-related activities (for example, walking to or from the bathroom or bedside commode, reaching for toilet tissue, or exiting a soiled bed).
Researchers at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis interviewed all patients at one hospital who fell over a 13-week period and/or their family members and nurses. They also reviewed adverse event reports and medical records to identify the circumstances and patient characteristics involved in the first fall of the 183 patients who fell during the study period. The results of their study revealed that the average age of patients who fell was 63.4 years, but ages ranged from 17 to 96 years. Their study showed that 85% of falls occur in the patient's room, 79 % of falls occurred when the patients were not assisted, 59 % during the evening/overnight and 19 % while walking. Nearly half (44 percent) of patients were confused or disoriented at the time they fell.
In 81% of the patients general muscle weakness was very prevalent, 39% had diabetes, 36% had urinary frequency and 38% had lower extremity problems. Most of the patients who fell were on sedatives that could have contributed to a fall. Falls due to elimination-related activities increased the risk of fall-related injury; the patient was left alone after being assisted to the bathroom or commode. Many patients who fell did not use assistive devices that they regularly used at home.
Falls in the hospital affect nearly everyone and falls prevention programs are necessary to prevent hospital falls and reduce fall injury rates.
Falls Prevention Process
The Falls Risk Tool is incorporated into the computer flow sheet charting that the nurse does for each patient assessment. The nurse will obtain a falls risk score for their patients using this evidence based tool created by John Hopkins Hospital. This score is the result of several factors such as falls history, cognition, mobility, medications, and patient care equipment that place a patient a risk for a fall. A patient will be an automatic low risk for the following conditions: paralysis or complete immobilization. The nurse does not have to complete the rest of the falls risk tool for that patient, but needs to make sure that the low risk fall interventions are in place. Also a patient is an automatic high risk for the following conditions: history of more than one fall within 6 months before admission or patient has experienced a fall during this hospitalization. The nurse does not have to complete the rest of the numeric section of the falls tool in this case but needs to make sure that the FALLS RISK band, red falling star sign, falls sticker, and high risk interventions are in place. For all patients, complete the falls risk tool on admission, every 24 hours, after a fall, post procedure, transfer to another unit, and change in clinical condition which could increase the patient’s fall risk.
Obtain a Falls Risk Score based on your Assessment/Observation:
* Low Risk 0-5
* Moderate Risk 6 - 13
* High Risk > 13
Apply ORANGE falls risk arm band if the patient is a Falls Risk
Post “YELLOW” falling star visual if patient is a “MODERATE FALLS RISK” ( storage of these signs is individual for each unit so find out where these are stored on your unit)
Post “RED” falling star visual if patient is a“ HIGH FALLS RISK” (storage of these signs is individual for each unit so find out where these are stored on your unit)
Make sure the “FALLS RISK” sticker is on the patient’s chart & KARDEX (this is usually done by the HUC on your unit).
Follow the Falls Risk Interventions posted in patient room and review these interventions with the NA assigned to that falls risk patient.
If the doctor has not entered a fall risk order for the patient, the nurse needs to enter this order in COE.
Make sure to call the patient’s MD and quality track any patient falls. Also, document incident in the progress note of the patient’s chart. The nurse should also notify the patient’s family after a fall.
Document a post-fall assessment 8-24 hours after the fall. Make sure to address the patient’s physiological and mental status.
The posey sitter is an electronic device that can be used to assist with observation of patients. These units have also helped with the decrease in use of patient restraints and helped decrease the likelihood of patient falls. These units can be used in both the patient’s bed and chair. The nurse can order a posey sitter unit from CSR (these units are called Falls alarm under the CSR order screen). The sensor pads used to connect to the units are located in each unit’s storeroom. Operating directions for the posey sitter are included with each unit.
Management of Falls

Complete a falls risk tool on all patients at:
admission,
every 24 hours
after a fall, post procedure
upon transfer to another unit,
change in clinical condition which could increase fall risk,
PRN
Assessment History Medications Mobility Cognition Patient
Care Equipment
Moderate
Risk (Score
6 - 13)
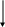
Follow
low risk management plan (White) Follow
moderate risk management plan (Yellow) Follow
high risk management plan
(Red)
FALLS RISK INTERVENTIONS
|
LOW FALLS RISK |
MODERATE FALL RISK |
HIGH FALL RISK |
|
Fall risk score = 0-5 points |
Fall risk score = 6-13 points |
Fall risk score = > 13 points |
|
Maintain safe unit environment : Remove excess equipment/supplies/ furniture from rooms & hallways. Coil and secure excess electrical and telephone wires. Clean all spills in patient room or in hallway immediately. Place a signage to indicate wet floor danger.
Follow the following safety interventions:
Orient the patient to surroundings, including bathroom location, use of call light. Keep bed in lowest position during use unless impractical (when doing a procedure on a patient) Keep the top 2 side rails up Secure locks on beds, stretcher & wheel chair. Keep floors clutter/obstacle free (especially the path between bed and bathroom/commode). Place call light & frequently needed objects within patient reach. Answer call light promptly. Encourage patient/family to call for assistance as needed. Assure adequate lightening especially at night. Use proper fitting non-skid footwear. |
Maintain safe unit environment : Remove excess equipment/supplies/ furniture from rooms & hallways. Coil and secure excess electrical and telephone wires Clean all spills in patient room or in hallway immediately. Place a signage to indicate wet floor danger.
Institute flagging system: 1. Apply falls risk arm band 2. Falling star (yellow)outside the door 3. Falls risk sticker on the medical record.
Follow low falls risk interventions plus:
Monitor & assist patient in following daily schedules:
Supervise/assist bedside sitting, personal hygiene and toileting as appropriate. Reorient confused patient as necessary. Establish elimination schedule and use of bedside commode if appropriate.
Evaluate need for: Pt consult if patient has a history of falls and /or mobility impairment. OT consult
|
Maintain safe unit environment : Remove excess equipment/supplies/ furniture from rooms & hallways. Coil and secure excess electrical and telephone wires Clean all spills in patient room or in hallway immediately. Place a signage to indicate wet floor danger.
Institute flagging system: 1. Apply falls risk arm band 2. Falling star (red) outside the door 3. Falls risk sticker on the medical record.
Follow low & moderate falls risk interventions plus:
REMAIN WITH PATIENT WHILE TOILETING Observe q 60 minutes unless patient is on activated bed or chair alarm. When necessary transport throughout hospital with assistance of staff or trained care givers. Consider bedside procedure.
Evaluate need for following measure going from less restrictive to more restrictive: Moving patient to room with best visual access to nursing station. Activated bed/chair alarm. 24 hour supervision/sitter Physical restraint- only with authorized prescriber order. |
METHODIST HOSPITAL
NURSING GUIDELINE: FALLS
AUTHOR/CREDENTIALS: Shamsah Rehmatullah, RN, MSN ACCOUNTABLE PARTY: Director of Professional Nursing Practice
ORIGIN DATE: 11/05 REVISION NUMBER: REVISION DATE: 05/06
|
OUTCOMES |
INTERVENTIONS |
|
1. Patients will be assessed/observed for falls risk on admission and daily
|
1. Recognize risk factors for falls: History of falls Muscle weakness Gait deficit Balance deficit Use of assistive device Visual deficit Arthritis Impaired ADL Cognitive impairment Delirium Dementia Parkinson’s disease Impaired mobility Patient care equipment Medication 2. Falls Risk Score: 0 - 5 Low Risk 6 - 13 Moderate Risk >13 High Risk 3. Identify patients at falls risk. Assess patients for falls Complete the falls risk score based on risk factors on admission Apply Falls Risk Band on Patients at Moderate or High Risk Place Falling Star visual outside the door * Yellow for moderate risk *Red for high risk Place falls risk sticker on patients chart Initiate the interventions based on the level of risk
|
|
2. Patients at risk for falls will receive appropriate intervention. |
Interventions for all patients
Keep the call light within reach – assure patient is able to use Keep bed in low position/ brakes locked Side rails in position Non-slip footwear / assess gait - assist if needed Assistance with elimination
Maintain safe unit environment : Remove excess equipment/supplies/ furniture from rooms & hallways. Coil and secure excess electrical and telephone wires. Clean all spills in patient room or in hallway immediately. Place a signage to indicate wet floor danger.
Low Risk 0 - 5 Orient the patient to surroundings, including bathroom location, use of call light. Keep bed in lowest position during use unless impractical (when doing a procedure on a patient) Keep the top 2 side rails up. Secure locks on beds, stretcher & wheel chair. Keep floors clutter/obstacle free (especially the path between bed and bathroom/commode). Place call light & frequently needed objects within patient reach. Answer call light promptly. Encourage patient/family to call for assistance as needed. Assure adequate lightening especially at night. Use proper fitting non-skid footwear.
2. Moderate Risk 6- 13. Above interventions plus Monitor & assist patient in following daily schedules: Supervise/assist bedside sitting, personal hygiene and toileting as appropriate. Reorient confused patient as necessary. Establish elimination schedules and use of bedside commode if appropriate. PT / OT consult if patient has history of falls and /or mobility impairment. 3. High Risk >13. Above interventions plus Follow low & moderate falls risk interventions plus: REMAIN WITH PATIENT WHILE TOILETING Observe q 60 minutes unless patient is on activated bed or chair alarm. When necessary transport throughout hospital with assistance of staff or trained care givers. Consider bedside procedure. Notify receiving area of high fall risk.
Evaluate need for following measure going from less restrictive to more restrictive: Moving patient to room with best visual access to nursing station. Activated bed/chair alarm 24 hour supervision/sitter Physical restraint-only with authorized prescriber order.
|
RELATED DOCUMENTS
John Hopkins Hospital
REFERENCE MATERIALS:
Gillespie, L.D., Gillespie, W.J., Robertson, M.C., Lamb, S.E., & Cumming, R.G., Rowe, B. H. (2003). Interventions for preventing falls in elderly people (Cochrane Review). The Cochrane Library, Issue 2.
McInnes, L., Gibbons, E., Chandler-Oatts, J. (2005). Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Assessment and Prevention of Falls in Older People. Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing, 2(1), 33-36.
Perell, K.L., Nelson, A., Goldman, R.L., Luther, S.L., Prieto-Lewis, N., & Rubenstein, L.Z. (2001). Fall risk assessment measures: An analytic review. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 56, M761-M766.
JCAHO. (2002). Sentinel Event Alert. Bed rail-related entrapment deaths. Sentinel Event Alert, 27,1-3.
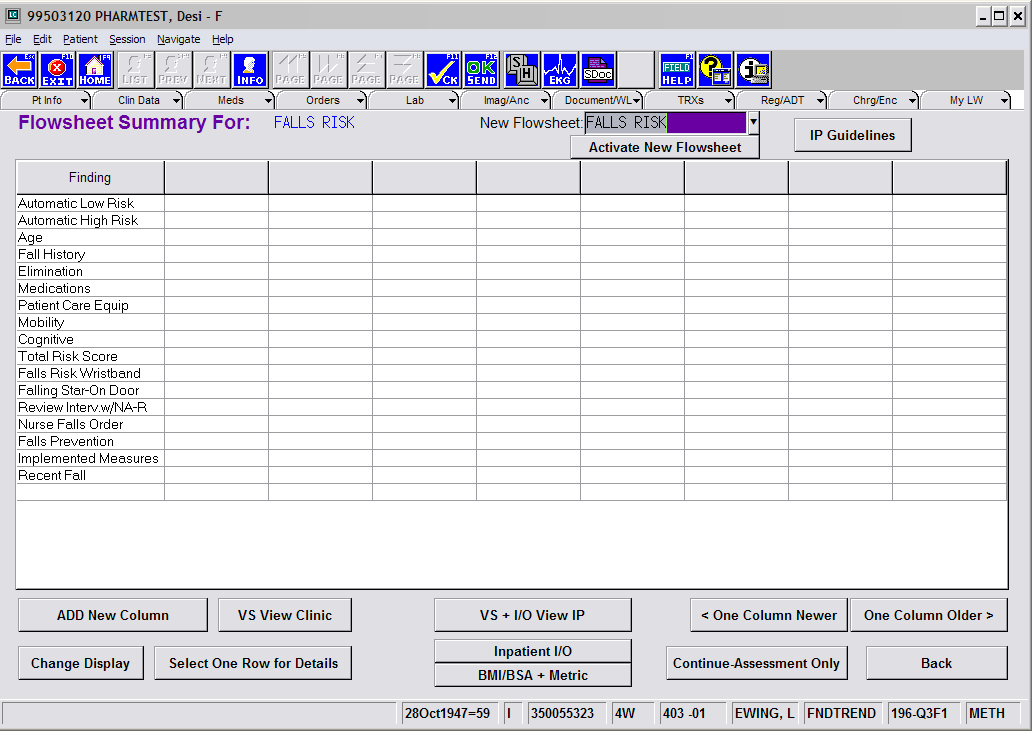
Example of Falls flowsheet listed in last word.
Falls Prevention Process
PLEASE SIGN THIS SHEET AND RETURN TO YOUR NURSE MANAGER /ASSOCIATE NURSE MANAGER/ ASSISTANT NURSE MANAGER.
Complete Falls Risk Tool on all patients on admission, daily & PRN
Obtain a Falls Risk Score based on your Assessment/ Observation:
Low Risk 0-5
Moderate Risk 6 - 13
High Risk > 13
Apply ORANGE falls risk arm band if the patient is a Falls Risk
Post “YELLOW” falling star visual if patient “MODERATE FALLS RISK”
Post “RED” falling star visual if patient is “ HIGH FALLS RISK”
Make sure a “FALLS RISK” sticker is on the patient’s chart & KARDEX
Follow the Falls Risk Interventions posted in patient room
I have read the enclosed Falls risk self-learning packet and understand my role in helping to prevent falls for patients.
Name: ________________________________________
Employee ID #____________________________
Unit____________________________
Date______________________________
FALLS RISK QUIZ
Please circle the correct answer.
A patient with a falls risk score of 6-13 indicates a
Low falls risk
Moderate falls risk
High falls risk
The nurse should complete a falls risk assessment every
4 hours
8 hours
24 hours
If a patient is paralyzed or completely immobilized, they are a(n)
Automatic low falls risk
Automatic moderate falls risk
Automatic high falls risk
A yellow falling star sign indicates
Low falls risk
Moderate falls risk
High falls risk
A red falling star sign indicates
Low falls risk
Moderate falls risk
High falls risk
After a patient falls, the nurse should
Scold the patient
Do nothing
Call the patient’s MD, complete a quality tracking report, and document the incident in a progress note in the patient’s chart.
Post-fall documentation should be done in a progress note in the patient’s chart
6-8 hours after a fall
8-24 hours after a fall
not at all
The intervention of remaining with a patient while toileting is a
Low risk intervention
Moderate risk intervention
High risk intervention
An orange falls risk arm band, yellow or red falling star, and falls risk sticker on the patient’s chart and kardex are needed for all patients who are
Low/moderate falls risk
Moderate/high falls risk
Low/high falls risk
What electronic unit can be ordered from CSR to help assist with observation of a patient, decrease use of restraints, and decrease the likelihood of a fall?
Posey sitter
Posey restraint
Posey hugger
Answers to the Falls Risk Quiz
b- low falls risk scores are 0-5, moderate falls risk scores are 6-13, and high falls risk scores are >13.
c- Scores are to be completed on admission, every 24 hours, after a fall, post procedure, transfer to another unit, and any change in patient’s condition.
a- If a patient is paralyzed or completely immobilized, the patient is an automatic low falls risk. There is no automatic moderate falls risk. If a patient has a history of more than one fall within 6 months before admission or patient has experienced a fall during this hospitalization, the patient is an automatic high falls risk. Remember, the nurse does not have to complete the numerical part of the tool if the patient is deemed an automatic low or high falls risk.
b- Moderate falls risk patients are to have a yellow falling star sign on their room door.
c- High falls risk patients are to have a red falling star sign on their room door.
c- With every fall, the nurse needs to call the patient’s MD, complete a quality tracking report, and document the incident in a progress note of the patient’s chart.
b- Post fall documentation need to take place 8-24 hours after the fall. This documentation should be completed in a progress note in the patient’s chart. The nurse should address the patient’s physiological and mental status.
c- see the list of interventions listed on the FALLS RISK INTERVENTIONS chart.
b- Moderate and high falls risk patients require these actions.
a- The posey sitter is the electronic device used to help assist with observation of a patient, decrease use of restraints, and decrease likelihood of a fall.
21 FALLS COSTS NUMBERS AND LINKS WITH VISUAL
25 WHAT IS SCIENCE? METHODOLOGICAL PITFALLS UNDERLYING THE EMPIRICAL
27 LAFAYETTE ROAD HAMPTON FALLS NH 03844 WWWLUCKYDOGDAYCARENHCOM 6035120241
Tags: falls risk, high falls, falls, rnlpn, commission, joint, guide
- AGENDA CONSULTATION ON THE IMPACT OF FREE TRADE AND
- 15 LISTES DES CHAMPIGNONS À BELLE – ILE –
- DEAR FRIENDS OF THE ASSOCIATION OF HOLOCAUST SURVIVORS IN
- 2 DEPARTAMENTO JURIDICO K 7263 (1339) 2014 ORD Nº
- 1 PHYSICS OF BIOLOGICAL SYSTEMS CONRAD ESCHER HANSWERNER
- 74 TEHNIČNO POROČILO 741 TEHNIČNI OPIS PREDVIDENIH DEL 7411
- 7 KASIM 1989 KUZEY KIBRIS TÜRK CUMHURIYETI CUMHURIYET MECLISI’NIN
- ALOITE PAIKKAKUNNAN NIMI KUNNAN KAUPUNGIN TYÖNTEKIJÖINÄ TYÖSKENTELEVIEN ADOPTIOVANHEMPIEN
- 76 CAPÍTULO 4 4 IDENTIFICACIÓN ANÁLISIS Y GERENCIAMIENTO DE
- 1 PANTALLA INICIAL EN LA PANTALLA INICIAL APARECE
- LOS RIESGOS DE UNA MEMORIA INCOMPLETA TZVETAN TODOROV EL
- LINK TO CIM0107 LINK TO CIM0109 VIOLATIONS OF SECTION
- a Psicologia da Apresentação por Slides por jon Hanke
- [YOUR LOGO] CONTACT [CONTACT NAME] TEL [CONTACT TELEPHONE] EMAIL
- PLAN VEŽBE 3 ZA POTREBE REALIZACIJE PRAKTIČNIH VEŽBI NA
- SPECTROSCOPY PURDUE UNIVERSITY INSTRUMENT VAN PROJECT BRASS ANALYSIS PURPOSE
- W SWS OFFICER AND COMMITTEE REPORT (HAWAII MEETING 2010)
- MVD 21VIII2007 ESTIMADO FERNANDO FELICITO TU BENEMÉRITA OBRA EN
- VLADA REPUBLIKE HRVATSKE NA TEMELJU ÈLANKA 49A ZAKONA O
- 2 TEMA 9 LA CRISIS DEL ANTIGUO RÉGIMEN 91
- USTAWA Z DNIA 2017 R O ZMIANIE USTAWY O
- SILABUS PENDIDIKAN TEKNIK BANGUNANS1 SEMESTER V SILABUS 1 IDENTITAS
- NANÁ VASCONCELOS BIOGRAPHY IN THE YEAR 1956 BORN IN
- PAIN AND JOY SPARKS SIMMERING SPIKES LANCING INVADE THE
- SEKCE A – PRODUKTY A SLUŽBY ZEMĚDĚLSTVÍ LESNICTVÍ A
- STRONA 6 ZAŁĄCZNIK NR 1 – FORMULARZ LISTU
- OIK1101572018KJIK WROCŁAW DNIA 17 GRUDNIA 2018 R DYREKTOR OKRĘGOWY
- LISTA JUZGADO CIVIL 3 110811 2493 CARABAJAL MARIA CARMEN
- CURZON ROAD MEDICAL PRACTICE PATIENT PARTICIPATION GROUP THE PRACTICE
- MOORE TIMOTHY MOORE TIMOTHY INSTRUCTOR MRS TAMMY MOORE CLASS
LIDIJA HOČEVAR PREDSEDNICA SVETA STARŠEV JVIZ OŠ DOBREPOLJE VIDEM
4 RENTA – ACTUAL LEY SOBRE IMPUESTO A LA
 AIRPORTS AIRPORTS ARE DIVIDED INTO LANDSIDE AND AIRSIDE AREAS
AIRPORTS AIRPORTS ARE DIVIDED INTO LANDSIDE AND AIRSIDE AREAS (COMPANY’S LETTER HEAD) APPLICATION FOR SNI MARKING PRODUCT CERTIFICATION
(COMPANY’S LETTER HEAD) APPLICATION FOR SNI MARKING PRODUCT CERTIFICATIONCURSO INYECCIÓN ELECTRÓNICA DE GASOLINA OBJETIVO EL PARTICIPANTE
SECRETARÍA DE EXTENSIÓN UNIVERSITARIA DENOMINACIÓN DISEÑO Y DESARROLLO WEB
TÍTULO 37 – AQUISIÇÃO DE SEMENTES DOCUMENTO 5 –
USE OF MILK POWDER IN EMERGENCIES ‑ OXFAMS POSITION
CUATRO ACTITUDES QUE FAVORECEN LA CULTURA DE LA DIVERSIÓN
ITGAUM 2006 PRELIMINARY AGENDA TUESDAY JUNE 13 400 PM
PROTOCOLE AUTOPHARM DÉPISTAGE DE L’HTA PAR LES PHARMACIENS AVEC
 PRESS RELEASE THE ARCHITECTURAL PROJECT MORE THAN JUST A
PRESS RELEASE THE ARCHITECTURAL PROJECT MORE THAN JUST A ORD Nº 5506367 MATERIA ORGANIZACIONES SINDICALES CUOTA SINDICAL MODIFICACIÓN
ORD Nº 5506367 MATERIA ORGANIZACIONES SINDICALES CUOTA SINDICAL MODIFICACIÓN 5 STATISTICS AND RESEARCH METHODS STATISTICS AND RESEARCH METHODS
5 STATISTICS AND RESEARCH METHODS STATISTICS AND RESEARCH METHODSMODELARSKI KLUB BRATOV RUSJAN VIPAVSKA CESTA 144 5000 NOVA
 TUTORIAL ON OPTOMECHANICAL BEAM STEERING MECHANISMS OPTI 521 TUTORIAL
TUTORIAL ON OPTOMECHANICAL BEAM STEERING MECHANISMS OPTI 521 TUTORIAL 555 WINPRO ONLINE 2000 RELEASE NOTES
555 WINPRO ONLINE 2000 RELEASE NOTESFINAL VERSION TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SERVICE – SPECIALTY
 EXPLODED VIEW SYNUS SELF SERVICE GENERAL SPLITTING UP 1
EXPLODED VIEW SYNUS SELF SERVICE GENERAL SPLITTING UP 1 DÜZCE ÜNİVERSİTESİ SAĞLIK BİLİMLERİ FAKÜLTESİ HEMŞİRELİK BÖLÜMÜ HEMŞİRELİK ESASLARI
DÜZCE ÜNİVERSİTESİ SAĞLIK BİLİMLERİ FAKÜLTESİ HEMŞİRELİK BÖLÜMÜ HEMŞİRELİK ESASLARI