TITLECLUSTERING OF NEURONAL K+CL COTRANSPORTER IN THE LIPID RAFTS
TITLECLUSTERING OF NEURONAL K+CL COTRANSPORTER IN THE LIPID RAFTS
The dendritic spine of layer V pyramidal neuron in contralateral area of focal ischemia was actively remodeling in somatosensory cortex
Title:Clustering of neuronal K+-Cl- cotransporter in the lipid rafts by tyrosine phosphorylation
Authors: Miho Watanabe, Hiroaki Wake, Junichi Nabekura
Department/Division, University/Institute: Division of Homeostatic Development, National Institute for Physiological Sciences, Okazaki, 444-8585, Japan,
Abstract:
.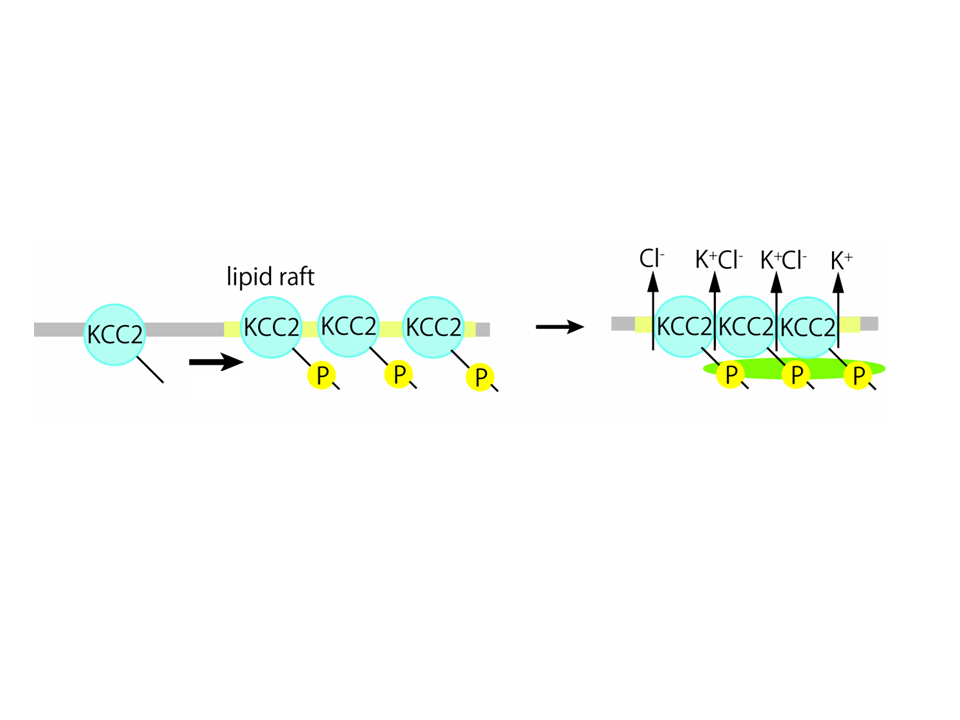 KCC2 is a principal molecule to exclude Cl-
out of the neurons and contributes to the maintenance of low [Cl-]i.
The mechanisms regulating KCC2 function have important implications
for understanding the plasticity of GABA and glycine-driven
inhibitory transmission. In addition to an increasing the evidences
of the long term regulation of KCC2 protein in development and
damaged neurons, much attention has been recently paid to a rapid and
dynamic alteration of KCC2 function. However, less is known regarding
the regulation of KCC2 molecule directly linked to appear its
function. KCC2 contains one consensus of a tyrosine protein kinase
phosphorylation site located at the long carboxy terminal. Genistein,
tyrosine kinase inhibitor, shifted EGABA
to more depolarized values and induced translocation of KCC2 from
punctate stainings to more uniform distribution in the hippocampal
neurons. Mutation of the tyrosine kinase amino acid residue (Y1087D)
also reduced KCC2 activity and abolished its punctate distribution
along the membrane, indicated that phosphorylated KCC2 form cluster
in restricted membrane domain. Sodium vanadate, a tyrosine
phosphatase inhibitor, increased the proportion of KCC2 associated
with lipid rafts, suggesting that phosphorylation of KCC2 facilitated
the interaction of this molecule with lipid rafts. Furthermore, loss
of tyrosine phosphorylation reduced oligomerization of KCC2,
indicating that tyrosine phosphorylation is required for KCC2
oligomerization. Deletion of 28
amino acid residue in carboxy terminal of KCC2 did not show
clustering and oligomer.
These results suggest that KCC2 forms cluster by tyrosine
phosphorylation via carboxy terminal, thereby extrude Cl-
efficiently to maintain local Cl-
low.
KCC2 is a principal molecule to exclude Cl-
out of the neurons and contributes to the maintenance of low [Cl-]i.
The mechanisms regulating KCC2 function have important implications
for understanding the plasticity of GABA and glycine-driven
inhibitory transmission. In addition to an increasing the evidences
of the long term regulation of KCC2 protein in development and
damaged neurons, much attention has been recently paid to a rapid and
dynamic alteration of KCC2 function. However, less is known regarding
the regulation of KCC2 molecule directly linked to appear its
function. KCC2 contains one consensus of a tyrosine protein kinase
phosphorylation site located at the long carboxy terminal. Genistein,
tyrosine kinase inhibitor, shifted EGABA
to more depolarized values and induced translocation of KCC2 from
punctate stainings to more uniform distribution in the hippocampal
neurons. Mutation of the tyrosine kinase amino acid residue (Y1087D)
also reduced KCC2 activity and abolished its punctate distribution
along the membrane, indicated that phosphorylated KCC2 form cluster
in restricted membrane domain. Sodium vanadate, a tyrosine
phosphatase inhibitor, increased the proportion of KCC2 associated
with lipid rafts, suggesting that phosphorylation of KCC2 facilitated
the interaction of this molecule with lipid rafts. Furthermore, loss
of tyrosine phosphorylation reduced oligomerization of KCC2,
indicating that tyrosine phosphorylation is required for KCC2
oligomerization. Deletion of 28
amino acid residue in carboxy terminal of KCC2 did not show
clustering and oligomer.
These results suggest that KCC2 forms cluster by tyrosine
phosphorylation via carboxy terminal, thereby extrude Cl-
efficiently to maintain local Cl-
low.
Tags: cotransporter in, lipid, cotransporter, rafts, neuronal, titleclustering
- RECIBÍ DATOS DE LA ASOCIACIÓN NOMBRE DE LA ENTIDAD
- INTEGRACIÓN DE VARIABLES DEL TRANSPORTE EN EL DESARROLLO CONCURRENTE
- ŠTEVILKA 6033182018 DATUM 2132019 SVET NACIONALNE AGENCIJE REPUBLIKE SLOVENIJE
- SPISAK ODOBRENIH RADNIH UDŽBENIKA UDŽBENIKA PRIRUČNIKA RADNIH LISTOVA I
- ESTADO DO RIO GRANDE DO SUL EMPENHOS EMITIDOS 14
- MARKET PARTICIPANTS IN TAIWAN SECURITIES MARKET SECURITIES INVESTMENT CONSULTING
- BASIN BÜLTENI 2 NISAN 2012 USAŞ EGE KRAFT’LA BIRLEŞIYOR
- YOUR USE OF ANY DATA COVERED BY THIS AGREEMENT
- 103RD SESSION OF THE INTERNATIONAL LABOUR CONFERENCE (28 MAY
- PRIMER 3 DATA JE SLEDEĆA ŠEMA BAZE PODATAKA S
- PARTNERSHIPS IN SCIENCE PROJECTS IN SLOVENIA APPLICATION FORM 2007
- 99 INDEPENDENT AGENCIES NOT PART OF STATE GOVERNMENT
- ESTUDIO DE HISTORIA DE UNA ESCALERA EN 1949 PRESENTÓ
- SECTION 4 LES PROPRIÉTÉS CONCURRENTES IL EXISTE DES
- SEGREVANJE TELES S TOPLOTO VAJE 1 KOLIKŠNA TOPLOTA
- JUNTA RECURSAL DO PROGRAMA ESTADUAL DE PROTEÇÃO E DEFESA
- VACANCY ANNOUNCEMENT QUITMAN SCHOOL DISTRICT 104 EAST FRANKLIN STREET
- SAMPLE TRUST PROTECTOR PROVISIONS 1GLENN KARISCH’S TRUST PROTECTOR PROVISIONS
- FICHA ALTA PATRONOSAS ACEPTO SER PATRONOA DE LA FUNDACIÓN
- BOLOGNA SÜRECİ UYUM ÇALIŞMALARI PROGRAM BİLGİ PAKETİ VE DERS
- ACTA NUMERO TRESCIENTOS TREINTA Y SIETE GUIÓN DOS MIL
- VERSION DECEMBER 2017 USAGE EXCLUSIF DU BÉR POUR
- OBRAZAC OPK OBRAZAC ZA PROCJENU KVALITETE PRIJAVE EVALUACIJSKI KRITERIJI
- CAMPAÑA IVA HERRAMIENTA DE DIAGNÓSTICO RONDA DE PREGUNTAS 25052010
- POVJERENSTVO ZA PROVEDBU JAVNOG NATJEČAJA ZA PRIJAM VJEŽBENIKAVJEŽBENICE U
- THE PROMOTION EVENT PRESENTING INNER MONGOLIA AUTONOMOUS REGION AGENDA
- OBAVIJEST O PROMJENI TERMINA INFORMATIVNE RADIONICE PROMIJENJEN JE
- 22 (22) SAMMANTRÄDE MED MILJÖ OCH KONSUMENTNÄMNDEN SAMMANTRÄDESDATUM 29
- PROGRAMA BIZKAIA CREATIVA 2012 MEMORIA DE PROYECTO DE EMPRESA
- [EXASOL2703] SNAPSHOT EXECUTION MODE FOR METADATA QUERIES (PREVIEW FEATURE)
 IL GIORNO E LE STAGIONI RE COME L’AURORA AL
IL GIORNO E LE STAGIONI RE COME L’AURORA ALBIOGRAFIA DON LUIGI CIOTTI NASCE IL 10 SETTEMBRE 1945
‑ 2 ‑ 18ª SESIÓN POR QUÉ ES IMPORTANTE
UCHWAŁA NR XXXVI2672017 RADY POWIATU TCZEWSKIEGO Z DNIA 19
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE SDPER21 NATURAL RESOURCES CONSERVATION
STATUT SZKOŁY PODSTAWOWEJ Z ODDZIAŁAMI INTEGRACYJNYMI NR 144 W
 U NOFFICIAL COMMENT FORM — PROTECTION SYSTEM MAINTENANCE AND
U NOFFICIAL COMMENT FORM — PROTECTION SYSTEM MAINTENANCE ANDNA PODLAGI 72 ČLENA STATUTA OBČINE ŠOŠTANJ (URADNI LIST
 SECTION 28 31 91A FIRE ALARM SYSTEM DESCRIPTION PAGE
SECTION 28 31 91A FIRE ALARM SYSTEM DESCRIPTION PAGEHAARLEM BREEDBANDSTAD HERBERT BLANKESTEIJN KPN NEEMT HEEL HAARLEM OP
GUIA PER A LA INCORPORACIÓ DEL CURRÍCULUM NUCLEAR A
OFFICIAL USE ONLY – PRIVACY ACT INJURYILLNESS INVESTIGATION TOOL
REAL DECRETO 18391997 DE 5 DE DICIEMBRE POR EL
 7491 INTEGER СОЗДАЙТЕ КЛАСС INTEGER СОГЛАСНО СЛЕДУЮЩЕЙ ДИАГРАММЕ
7491 INTEGER СОЗДАЙТЕ КЛАСС INTEGER СОГЛАСНО СЛЕДУЮЩЕЙ ДИАГРАММЕJUNTA DE ANDALUCÍA CEIP ANTONIO MACHADO MÁLAGA VI PROCEDIMIENTOS
 ORGANIZATION OF AMERICAN STATES GENERAL ASSEMBLY FORTYFIRST REGULAR SESSION
ORGANIZATION OF AMERICAN STATES GENERAL ASSEMBLY FORTYFIRST REGULAR SESSION19 DIANE VAUGHAN CURRICULUM VITAE JANUARY 2021 DEPARTMENT
ЈКП „ТРЖНИЦА“ НИШ ЂУКЕ ДИНИЋ БР 4 НА
ATTO DI INDIRIZZO SULLA PUBBLICITÀ INFORMATIVA DELLE ATTIVITÀ PROFESSIONALI
 SPECYFIKACJA ISTOTNYCH WARUNKÓW ZAMÓWIENIA W POSTĘPOWANIU O UDZIELENIE ZAMÓWIENIA
SPECYFIKACJA ISTOTNYCH WARUNKÓW ZAMÓWIENIA W POSTĘPOWANIU O UDZIELENIE ZAMÓWIENIA