T AKAHIRO ITOH GRADE MASTER COURSE STUDENT 2ND GRADE
T AKAHIRO ITOH GRADE MASTER COURSE STUDENT 2ND GRADE
Japan-Korea Inorganic Symposium
T akahiro
ITOH
akahiro
ITOH
Grade: Master course student, 2nd grade (M2)
Affiliation: The Graduate University for Advanced Studies [SOKENDAI]
Address: Higashiyama 5-1, Myodaiji, Okazaki, Aichi 444-8787 Japan
Phone: +81-564-59-5587 Fax: +81-564-59-5589
E-mail: titoh@ims.ac.jp
Date of Birth 1989.10.14.
Sex Male
Education
2008 – 2012 B. S. Nagoya University
2012 – present The Graduate University for Advanced Studies [SOKENDAI]
Publications
"Arene-perfluoroarene Interactions for Crystal Engineering of Metal Complexes: Controlled Self-assembly of Paddle-wheel Dimers", T. Itoh, M. Kondo, M. Kanaike, and S. Masaoka, CrystEngComm, 2013, in press.
"Dispersed
Ru Nanoclusters Transformed from a Grafted Trinuclear Ru Complex on
SiO2
for Selective Alcohol Oxidation"
S. Muratsugu, M. H. Lim,
T. Itoh, W. Thumrongpatanaraks, M. Kondo, S. Masaoka, T. S. A. Hor,
and M. Tada, Dalton
Trans., 2013,
in press.
Presentations and Awards
Takahiro Itoh, Masaya Okamura, Go Nakamura, Mio Kondo, Shigeyuki Masaoka, “Syntheses, Structures and Redox Reactions of Rh(II) Paddlewheel Dimer Complexes with Complementary Interactions”, Nagoya Symposium 2013, Nagoya, Japan, May, 2013
Takahiro Itoh, Masaya Okamura, Go Nakamura, Mio Kondo, Shigeyuki Masaoka, “Complementary Interactions in Crystal Engineering : Syntheses, Structures and Redox Reactions of Rh(II) Paddlewheel Dimer Complexes, 2013 Asian Core Winter School, Busan, Korea, January, 2013
Research Interests
Multielectron Transfer Reaction Catalyzed by Transition Metal Complexes
Coordination Chemistry toward Artificial Photosynthesis
Thermal and Photochemical Activations of Small Molecules by Transition Metal Complexes
Construction of New Supramolecular Structures via Arene-perfluoroarene Interactions: Controlled Self-assembly of Paddle-wheel Complexes
Control over the self-assembling process of metal complexes is of key importance to construct supramolecular materials and nano devices, which have unique physical and chemical properties. Paddle-wheel complexes consisting of two metal ions and four monoanionic bidentate ligands attract much attention because of their highly symmetric (D4h) structure suitable for the construction of continuous structure. In this study, we aimed to construct supramolecular architectures using paddlewheel dimer units via multipoint arene-perfluoroarene interactions.
Figure
1 Controlled
self-assembly
of paddle-wheel
complexes
via arene-perfluoroarene
interactions
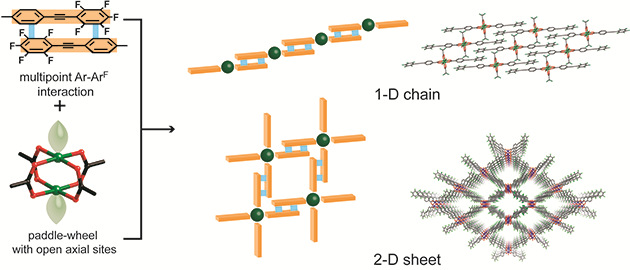
References
T. Itoh, M. Kondo, M. Kanaike, and S. Masaoka, CrystEngComm, 2013, in press.
Tags: grade (m2), grade, course, master, akahiro, student
- (DEĞIŞIKRG231201428891) EK PORTFÖY SINIRLAMALARINA UYUMUN KONTROLÜNE İLİŞKİN KONSOLİDE OLMAYAN
- SECTION 14 42 16 VERTICAL WHEELCHAIR LIFTS DISPLAY HIDDEN
- ALLA PROVINCIA DI BRINDISI SEGNALAZIONE CERTIFICATA DI INIZIO ATTIVITA’
- CONTENIDO EN ALÉRGENOS DE CADA PLATO [INCLUYA AQUÍ EL
- DOKUMENT POTWIERDZAJĄCY RECYKLING ZA ROK A PRZEZNACZONY DLA
- JULSHOW LÖRDAGEN DEN 13 DECEMBER OCH SÖNDAGEN DEN 14
- VER10 16012019 DECLARATION ON SMART CARD LOSS OR THEFT
- PROTOKÓŁ ZDAWCZO ODBIORCZY PRZEKAZANIA ODDZIAŁU ZNP W ……………………………………………………………………
- GOVERNING STRATEGIC ALLIANCES THE STRUCTURE AND PURPOSE OF ALLIANCE
- 0 COMUNICADO DE PRENSA LA ASAMBLEA DE
- 37 CAPÍTULO 1 1 FUNDAMENTOS TEÓRICOS 11 PLANTEAMIENTO DEL
- 5 REPORT ON THE SEMINAR WITH INTERNATIONAL PARTICIPATION DEVELOPMENT
- INCORPORACIÓN DE LAS NUEVAS TECNOLOGÍAS DECLARACIÓN FINAL LOS PRESIDENTES
- HEMATOLÓGIAI OSZTÁLY DR DOMBI J PÉTER FOLYÓIRATBAN MEGJELENT KÖZLEMÉNYEK
- OPIS DO PROJEKTU ZAGOSPODAROWANIA TERENU DZIAŁEK O NUMERACH EWIDENCYJNYCH
- FACULTAD DE CIENCIAS JURÍDICAS CARRERA DE DERECHO 1 TÍTULO
- KENDİ İSTEĞİ İLE KAYIT SİLME (EDEVLET) DİLEKÇE FORMU DOKÜMAN
- ALTERNATE ASSIGNMENT FOR SCHINDLER’S LIST OSKAR SCHINDLER WAS JUST
- R ELACIONES BINARIAS I DOS HOMBRES JUEGAN UN PARTIDO
- TYTUŁ POLSKI PRACY (14 PKT BOLD) TYTUŁ ANGIELSKI PRACY
- YABANCI UYRUKLU ÖĞRETİM ELEMANLARI İÇİN AÇIK KİMLİK FORMU (IDENTIFICATION
- HOW TO USE THIS TEMPLATE THIS TEMPLATE IS DESIGNED
- ENVIRONMENTAL STRATEGY SEP 2015 10 INTRODUCTION 11 THE UNIVERSITY’S
- WALIKOTA YOGYAKARTA DAERAH ISTIMEWA YOGYAKARTA PERATURAN WALIKOTA YOGYAKARTA NOMOR
- ARTÍCULO 316 Y SS DEL CÓDIGO PENAL DELITO CONTRA
- D110220773 ATTACHMENT 1 VERIFICATION OF ABORIGINAL ANDOR TORRES STRAIT
- 7 THE CONTRACTEE SHALL COMPLY WITH THE FOLLOWING REQUIREMENTS
- 28971 THE EVOLUTION OF DEVELOPMENT THINKING THEORY AND POLICY
- 28 JUNE 2019 SUBMISSION OF COMMENTS ON GUIDELINE ON
- TECHNICAL DATA SHEET NO 225 VERSION31ST OCT 2001 PAGE
 M TIMBRES FISCALES POR 100 COLONES UNICIPALIDAD DE PUNTARENAS
M TIMBRES FISCALES POR 100 COLONES UNICIPALIDAD DE PUNTARENASZAŁĄCZNIK NR 5 DO SIWZ WYKAZ WYKONANYCH ROBÓT
ZAPROŚ ŁĄKI KWIETNE DO SWOJEGO PROJEKTU W RAMACH BUDŻETU
TITRE CÉSARIENNE ET TROUBLES GÉNITOSEXUELS DU POSTPARTUM CESAREAN
CIRCULAR 0055 – 13112014 IMPORTANTE MODELO ESTRUCTURAL DE COSTOS
 LOS 20 NUEVOS QUIROPRÁCTICOS DEL CENTRO CATALÁN SE UNEN
LOS 20 NUEVOS QUIROPRÁCTICOS DEL CENTRO CATALÁN SE UNEN POLSKI ZWIĄZEK WĘDKARSKI O KRĘG GDAŃSKI KOŁO NR 74
POLSKI ZWIĄZEK WĘDKARSKI O KRĘG GDAŃSKI KOŁO NR 74 APRIL 2019 FREEDOM OF INFORMATION ACT (FOIA) REQUEST –
APRIL 2019 FREEDOM OF INFORMATION ACT (FOIA) REQUEST – RANK ANALYSIS OF THE ANISOTROPIC INVERSE CONDUCTIVITY PROBLEM JUAN
RANK ANALYSIS OF THE ANISOTROPIC INVERSE CONDUCTIVITY PROBLEM JUANINTRODUCCIÓN LA PROBLEMÁTICA AMBIENTAL GLOBAL EXIGE UN MANEJO SOSTENIBLE
 P LEXTALK LINIO POCKET INNFØRING NETTVERKSMAPPE PLEXTALK LINIO
P LEXTALK LINIO POCKET INNFØRING NETTVERKSMAPPE PLEXTALK LINIO JOB DESCRIPTION JOB TITLE LEGAL COUNSEL GRADE DE DEPARTMENT
JOB DESCRIPTION JOB TITLE LEGAL COUNSEL GRADE DE DEPARTMENT N HOUSING STATISTICAL RELEASE OCTOBER 2010 USING RESEARCH SUMMARY
N HOUSING STATISTICAL RELEASE OCTOBER 2010 USING RESEARCH SUMMARY 0 ES RUE BELLIARDBELLIARDSTRAAT 99 — 1040
0 ES RUE BELLIARDBELLIARDSTRAAT 99 — 1040 DELEGACIÓN DEL RECTOR PARA PROYECCIÓN INTERNACIONAL FRAME1 TÍTULO DEL
DELEGACIÓN DEL RECTOR PARA PROYECCIÓN INTERNACIONAL FRAME1 TÍTULO DEL C OLEGIO TÉCNICO PROFESIONAL NOCEDAL PROF ÓSCAR GARRIDO C
C OLEGIO TÉCNICO PROFESIONAL NOCEDAL PROF ÓSCAR GARRIDO C TISKOVÁ ZPRÁVA NADACE PARTNERSTVÍ ROSTE VE VAŠÍ OBCI STROM
TISKOVÁ ZPRÁVA NADACE PARTNERSTVÍ ROSTE VE VAŠÍ OBCI STROM ZAEP N° 113 ISLA HASSWELL PLAN DE GESTIÓN
ZAEP N° 113 ISLA HASSWELL PLAN DE GESTIÓNISRAEL FUENTE DE CULTURAS 8 DÍAS DESDE 1190
 MODELO SOLICITUD DE INTERVENTORA PARA LAS ELECCIONES A LA
MODELO SOLICITUD DE INTERVENTORA PARA LAS ELECCIONES A LA