IAEACN14252 THE ESTABLISHMENT AND PRACTICES OF TSOS FOR CHINESE
IAEACN14252 THE ESTABLISHMENT AND PRACTICES OF TSOS FOR CHINESE
The Establishment and Practices of TSOs for Chinese Nuclear Regulatory body
IAEA-CN-142/52
The Establishment and Practices of TSOs for Chinese Nuclear Regulatory Body
HAO Xiaofeng
State Environmental Protection Administration
(National Nuclear Safety Administration)
Beijing 100035, P.R.China
Abstract:Based on the requirements of Agency’s safety standard GS-R-1《Legal and governmental infrastructure for nuclear, radiation, radioactive waste and transport safety》 and more than twenty years’ practices in China, this paper presents the development of Technical Support Organizations (TSOs) of the Chinese nuclear regulatory body from the points of view of the practices, features, functions, challenges faced and counter measures etc.. The TSOs of the Chinese nuclear regulatory body have been founded and enhanced according to the continuously increased responsibilities and functions on nuclear safety supervision, and are aiming at providing full scale technical supports to the Chinese nuclear regulatory body in the areas of law making, nuclear safety review and evaluation, nuclear safety inspection, emergency preparedness and response, independent monitoring and check-up, scientific research, personnel training, quality assurance, information system establishing, international cooperation etc..
Key words: nuclear safety, supervision, technical support, functions
Introduction
More than 50 years’ history of peaceful use of atomic energy worldwide shows that atomic energy acts as a two-edged sword, while it is benefiting the human being, it may also bring the catastrophe to the human being if misgoverned. The Chernobyl nuclear accident not only caused enormous economic lost, but also left a deep shadow in the mind of the public. In this regard, the nuclear safety supervision differs from the governmental supervision on the traditional industries. Governments shall recognize the importance of the issue and take effective supervision modes and measures to protect the public and environment from the damage.
The use of atomic energy concerns a lot of high technology. So an effective nuclear safety supervision needs a powerful technical support. Moreover, many member states have developed their own nuclear safety supervision modes. In many member states, the staff number of nuclear safety regulatory bodies can only meet the basic requirements of some administrative management due to the limit of the scope of governmental infrastructures. In this context, more technical work has to be done by TSOs.
Many helpful practices and exploration have been performed worldwide and many useful experiences have been gained. A comprehensive international cooperation will be helpful to enhance the capacity of nuclear safety regulatory bodies and its TSOs, which conform to member states’ interests and will be helpful to achieve a consistently high safety level.
2. Responsibilities and functions of Chinese nuclear safety regulatory body
According to Agency’s safety standard GS-R-1《Legal and governmental infrastructure for nuclear, radiation, radioactive waste and transport safety》, the responsibilities and functions of regulatory body include defining policies, safety principles and associated criteria; establishing, promoting or adopting regulations and guides; reviewing and assessing submissions on safety from the operators; providing for issuing, amending, suspending or revoking authorizations; carrying out regulatory inspections; ensuring that corrective actions are taken if unsafe or potentially unsafe conditions are detected; and taking the necessary enforcement action in the event of violations of safety requirements.
The regulatory body may also have additional functions. Such functions may Include independent radiological monitoring in and around nuclear facilities; independent testing and quality control measurements; initiating, co-ordinating and monitoring safety related research and development work in support of its regulatory functions; providing personnel monitoring services and conducting medical examinations; monitoring of nuclear non-proliferation; and regulatory control of industrial safety.
Chinese nuclear regulatory body (National Nuclear Safety Administration-NNSA) has adopted almost all the responsibilities and functions mentioned above by GS-R-1. After more than 20 years’ practices, NNSA has formed its own infrastructure and supervision mode. The main responsibilities and functions of NNSA can be summarized as followings:
nuclear safety related law, policy and associated code, regulation and guide making;
nuclear safety related technical standard review;
nuclear safety review and evaluation;
nuclear safety inspection;
licensing process and enforcement ;
nuclear safety related accident investigation and treatment;
operational event evaluation and experience feedback;
emergency preparedness and response;
independent monitoring and check-up;
scientific research;
personnel training;
quality assurance;
public propaganda;
international cooperation etc.
These responsibilities and functions of NNSA may be extended or adjusted according to the real needs arising from our nuclear development in the near future.
3. Establishment and practices of TSOs for the Chinese nuclear regulatory body
Just at the beginning of the foundation of NNSA in 1984, we faced the challenge to perform the safety review for Qinshan and Daya Bay nuclear power plants. Very soon we realized that a temporarily organized review team could not satisfy the continuously increased needs arising from our nuclear development plan. We realized also the importance to establish our own technical support organization to provide full scale technical supports. So in 1989, NNSA established his own technical support organization: Nuclear Safety Center.
In 2006, Nuclear Safety Center was renamed to Nuclear and Radiation Safety Center. At present, this center has been developed to be a powerful technical support organization to NNSA with 14 divisions including legislation & information, reactor system & analysis, mechanical equipment & QA, electricity supply and I&C, siting & structure, radwaste management & fuel cycle, radiation protection & emergency response, nuclear installations operational safety, and radioactive sources safety etc.. The total staff number is going to be increased to 177 in several years.
The experts of the center have undertaken a lot of tasks of safety review, inspection, emergency response and scientific research etc. from NNSA. Some important work completed in the past include the safety review of Qinshan Phase II (Unit 1, 2, 3, & 4), Ling Ao (Unit 1, 2, 3, & 4) and Tianwan (Unit 1 & 2); the establishment of nuclear and radiation accident emergency response and evaluation system, nuclear installations operational experience feedback system, nuclear safety management data banks and nuclear safety information system etc..
Radiation Environment Monitoring Technical Center is one of the technical support organizations of State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA). Because NNSA was combined into SEPA in 1998, this center provides also the technical support to NNSA for independent radiological monitoring in and around nuclear facilities thereafter.
Beside the Nuclear and Radiation Safety Center and the Radiation Environment Monitoring Technical Center, NNSA has sought for assistance from some other organizations such as universities, research and design institutes. However, when these organizations provide technical support to NNSA, they must ensure the independence from organizations or bodies charged with the promotion of nuclear technologies or responsible for facilities or activities.
Suzhou Nuclear Safety Center (Suzhou Nuclear Power Research Institute Co. Ltd.) provides technical support to NNSA in the area of QA.
The major work of Nuclear Equipment Safety and Reliability Research Center (China Academy of Machinery Science and Technology) is to verify the availability of the nuclear component in which the non-conformity has occurred and provide enough technical proof to NNSA for their final administrative decision.
Beijing Nuclear Safety Review Center (Beijing Institute of Nuclear Engineering) provides technical support to NNSA on CANDU reactor safety review and operational management.
Tsinghua University provides technical support to NNSA in the area of PSA.
Shanghai Jiaotong University provides technical support to NNSA in the area of severe accident management.
Features of TSOs for the Chinese nuclear regulatory body
The orientation of TSOs in China is to provide comprehensive technical support to NNSA to fulfil effectively and efficiently its responsibilities and functions. This orientation decided some particular features as followings:
Independence from industries;
Non-profit and public welfare institutions;
Full funding from Government;
High technology and professional;
Special treatment policy needed to stabilize the team;
Independent audit calculation and testing capacity needed etc..
Functions of TSOs for the Chinese nuclear regulatory body
Except the administrative activities, the TSOs for the Chinese nuclear regulatory body assist NNSA comprehensively to discharge its assigned responsibilities and functions. Their functions concern the following areas:
Nuclear installations safety review, evaluation and inspection;
Environmental impact evaluation;
Operational events evaluation and experience feedback;
Emergency preparedness and response (including accident consequences evaluation and prediction);
Nuclear safety related law, policy and associated code, regulation and guide making;
Radwaste management;
Radiation protection;
Independent radiological monitoring in and around nuclear facilities
Nuclear material management;
Transport safety;
Nuclear pressurized equipment and components,
Radioactive sources management;
International cooperation;
Scientific research;
Training;
QA;
Developing independent audit calculation and testing capacity;
Nuclear safety engineer registration;
Nuclear safety information etc..
Challenges faced by the TSOs for the Chinese nuclear regulatory body
China is a developing country. Recently, we have launched an ambitious nuclear program. It is predicted that by the end of 2020, we will achieve the aim of 40,000MWe nuclear power capacity, which takes 4% of total national power capacity. That means we have to start the construction of at least two 1000MWe-units every year. The TSOs for the Chinese nuclear regulatory body are facing the big challenges:
Lack of competent staff;
Lack of enough financial support;
Lack of the experience to review the new generation nuclear power plant (AP1000, EPR);
Lack of independent audit calculation and testing capacity
Multiple designs with different techniques etc..
Counter measures available
NNSA and its TSOs have realized the challenges and prepared actively the counter measures.
The application for increasing the staff has been approved by the Government. We have set up a plan to recruit the new staff as soon as possible.
Recent years, we have gotten an increased financial support year after year from the Government. The problem of lack of enough financial support for the TSOs has been mitigated a lot.
We will reevaluate the real need on staff and finance based on the developing requirement, and strive for more support from the Government in order to create the necessary working conditions to improve the nuclear safety supervision capacity.
Facing the intense competition from the industries, we are studying the possibility to request special policy from the Government to avoid staff leaving, stabilize the team and absorb more skillful staff.
We are seeking for the cooperation with universities and industries for our staff training and education, and have gotten active responses. Moreover, we are contacting IAEA, Westinghouse and USNRC for staff training.
We are sure that a comprehensive international cooperation will be helpful for us to deal with the challenges, and improve the effectiveness, efficiency and level of our nuclear supervision.
end
Tags: chinese nuclear, the chinese, chinese, iaeacn14252, practices, establishment
- KONTAKT AKREDITACE EVA KOCIÁNOVÁ KUBELÍKOVA 27 130 00
- OBČINA ŠENTJUR JAVNI RAZPIS 2020 – POMOČ ZA OHRANJANJE
- EVALUACIÓN DE LA INVESTIGACIÓN PARA DOCENTES QUE APLICAN A
- KARTA OBIEGOWA DLA STUDENTÓW WYDZIAŁU NAUK POLITYCZNYCH I DZIENNIKARSTWA
- USING NIH COMMONS TO SUBMIT YOUR 2590 PROGRESS REPORT
- BILAG 21 UDARBEJDET UD FRA RAMMEBESKRIVELSE FOR DOKUMENTSTYRING I
- TRAIL CTC TRAINING 6268 THIRLWELL ROAD SHEFFIELD S8 9TF
- BAZI MENKUL SERMAYE İRATLARINA UYGULANAN İNDİRİM (ENFLASYONDAN ARINDIRMA) O
- D EPARTMENT OF HUMAN SERVICES SAFETY OVERSIGHT AND QUALITY
- WYKAZ OFERT ZŁOŻONYCH W RAMACH KONKURSU NR 12014 NA
- 7° JUZGADO CONSTITUCIONAL EXPEDIENTE 37536201401801JRCI07 MATERIA ACCIÓN
- I NSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO Y DE ESTUDIOS SUPERIORES DE OCCIDENTEAC
- ROSA CRISTINA VAZQUEZ CAN O CURRÍCULUM VITAE INFORMACIÓN PERSONAL
- PROYECTO SOBRE JORNADA CONTÍNUA CEIP MESTRE JOAQUÍN CARTAGENA CAMP
- JOB DESCRIPTION JOB TITLE EXECUTIVETEACHING FELLOW IN ECONOMICS &
- REPORT FOR THE REVIEW OF MBS COLONOSCOPY ITEMS –
- DECLARACIÓN RESPONSABLE DE REALIZACIÓN DE ACTIVIDADES DE FORMACIÓN
- 1º PRESENTACIÓN ORAL Nº ALUMNOA ASESOR FECHA HORA 1
- 3 ТЕРНОПІЛЬСЬКА ОБЛАСНА ДЕРЖАВНА АДМІНІСТРАЦІЯ РОЗПОРЯДЖЕННЯ ГОЛОВИ ОБЛАСНОЇ ДЕРЖАВНОЇ
- MATHEMATICS AND BEAUTY PAGE 35 MATHEMATICS AND BEAUTY NOVEMBER
- COLORADO STATE TREASURY FY21 PORTFOLIO DETAILTREASURY POOL 6302021 ASSET
- NOMBRE DE LA ACCIÓN CREAMOS RECURSOS DIDÁCTICOS PARA TRABAJAR
- METALAPSZABÁLY A MAGYAR ENDODONTIAI TÁRSASÁG ALAPSZABÁLYA 1 A TÁRSASÁG
- MEJORA DEL NIVEL DE SUSTANCIAS INDESEABLES CRITERIOS DE REDUCCIÓN
- ZASADY I TRYB PRZEPROWADZANIA POSTĘPOWANIA W SPRAWIE NOSTRYFIKACJI DYPLOMÓW
- A QUOI RESSEMBLE TA MAISON ? (GILLES PAUGET) JHABITE
- TC İSTANBUL 11 ASLÎYE CEZA MAHKEMESİ DEĞİŞİK İŞ NO
- LIST OF MSC AND PHD THESIS TITLES FOR FACULTY
- 219 EFEITO DA APLICAÇÃO DE AMINOÁCIDOS NA MANGUEIRA (MANGIFERA
- 41 THE ACCUSED AS A WITNESS1 WARNING!
 WOGA402 PAGE 2 E WOGA402 ORIGINAL ENGLISH DATE JULY
WOGA402 PAGE 2 E WOGA402 ORIGINAL ENGLISH DATE JULYEDITORIAL MESSAGE SPECIAL TRACK ON OUR TOPIC FIRST TRACK
PRÓBY PRACY WODNEJ REGULAMIN I EGZAMIN IRO
 NEW BOOK! EXTREME VALUE METHODS WITH APPLICATIONS TO FINANCE
NEW BOOK! EXTREME VALUE METHODS WITH APPLICATIONS TO FINANCEOTROCI V PRIMEŽU ZLORABE MOČI DOROTEJA LEŠNIK MUGNAIONI VIR
BOLETÍN OFICIAL DE LA PROVINCIA DIPUTACIÓN DE BADAJOZ ANUNCIO
 PRESS RELEASE 1ST SEPTEMBER 2008 EPISTEM AND ROTTAPHARM ANNOUNCE
PRESS RELEASE 1ST SEPTEMBER 2008 EPISTEM AND ROTTAPHARM ANNOUNCE O ANHSS LTCHA IMPLEMENTATION MEMBER SUPPORT PROJECT MODEL PURCHASED
O ANHSS LTCHA IMPLEMENTATION MEMBER SUPPORT PROJECT MODEL PURCHASEDADNAN MENDERES ÜNİVERSİTESİ STRATEJI GELIŞTIRME DAIRE BAŞKANLIĞI TAŞINIR İŞLEMLERİ
COLONIAL VILLAGE I LANDLORDTENANT CERTIFICATION REGARDING RESIDENT HANDBOOK THIS
 DATA EVALUATION RECORD ON THE TOXICITY OF [TGAI OR
DATA EVALUATION RECORD ON THE TOXICITY OF [TGAI ORADJUDICACIÓN DEFINITIVA DE MÓDULOS 2010 2011 ACTIVIDADES NÁUTICAS
 TC İSTANBUL ÜNİVERSİTESİ SAĞLIK BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ GEÇİCİ MEZUNİYET BELGESİ
TC İSTANBUL ÜNİVERSİTESİ SAĞLIK BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ GEÇİCİ MEZUNİYET BELGESİ 432024 99 Videoklipp 4 Ärenden som ska Fastställas i
432024 99 Videoklipp 4 Ärenden som ska Fastställas i POZVÁNKA NA SEMINÁŘ „MOŽNOSTI UPLATNĚNÍ ČESKÝCH SPOLEČNOSTÍ NA MEZINÁRODNÍM
POZVÁNKA NA SEMINÁŘ „MOŽNOSTI UPLATNĚNÍ ČESKÝCH SPOLEČNOSTÍ NA MEZINÁRODNÍM REGLAMENTO DEL ARTÍCULO 95 DE LA LEY FEDERAL DE
REGLAMENTO DEL ARTÍCULO 95 DE LA LEY FEDERAL DE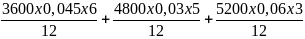 INTERETS SIMPLES BEP TERTIAIRE OBJECTIFS ÊTRE CAPABLE DE
INTERETS SIMPLES BEP TERTIAIRE OBJECTIFS ÊTRE CAPABLE DE 9 ATELIER 2019 DE LA PLATEFORME ETHIQUE ET BIOSCIENCES
9 ATELIER 2019 DE LA PLATEFORME ETHIQUE ET BIOSCIENCES Poziv-na-dostavu-ponuda-neov.revizija-DB-i-OHBP
Poziv-na-dostavu-ponuda-neov.revizija-DB-i-OHBPSONARCPROJECT JANPETER ER SONNTAG WÜRTTEMBERGISCHER KUNSTVEREIN STUTTGART PRESSEINFORMATION WÜRTTEMBERGISCHER