NAME INVERTEBRATE PHYLA NOTES PORIFERA PHYLUM A AN
14 INVERTEBRATE ASSESSMENT OF LOT 51 WILDE ALS SPRUIT17 TITLE A TOOLBOX FOR WORKING WITH LIVING INVERTEBRATES
7 WAMTS PRESERVATION AND LODGEMENT OF TERRESTRIAL INVERTEBRATE SPECIMENS
AN INVERTEBRATE WITH A SOFT UNSEGMENTED A AQUATIC MOLLUSK
BIOL 1407 INVERTEBRATES 2 MOLLUSKS AND ANNELIDS COMPARISONS 1
EFFECT OF GLYPRO HERBICIDE ON THE AQUATIC MACROINVERTEBRATE COMMUNITY
Name: ________________________________________
Name: ________________________________________
Invertebrate Phyla Notes
Porifera Phylum
a. An example of a Porifera is a _____sponge____________.
b. Porifera are considered the _____simplest______________ animals on the planet because they
were the earliest and are made up of only ______cells____________.
c. Porifera are sessile and live in _____water___________________.
d. The body of the sponge is covered in tiny openings called ______pores____________.
e. Water brings ____food______ and _______oxygen______ in through the pores and
________waste__________ out through the hole at the top called the ______osculum____.
f. Porifera reproduce sexually with ______sperm_____ and _______egg________ and
asexually by _______budding_______.
g. Porifera have ____no_______ symmetry or asymmetry.
h. Because the cells of a Porifera have an attraction to each other, they can ___pull themselves back
together_________ when separated. If a section moves too far away from the original sponge,
it will _____make a new sponge_____.
Cnidarian Phylum (used to be called Coelenterate)
a. The four kinds of Cnidarians are ____hydra_________, ________coral______,
________sea anemone__________, and _______jellyfish____________.
b. Cnidarians are made up of _______cells_______ and ________tissues________.
c. Most cnidarians live in _____ salt water (ocean)___________, but the hydra lives in
_____fresh water______________.
d. Hydra and jellyfish are mobile and chase after their food. Coral and sea anemones are sessile. They
must work with something to help bring their food to them. The sea anemone lives with
________clownfish_________ and coral live with ________algae________.
e. Cnidarians have ______radial_______ symmetry. This means that their body radiates out
from a center point (like drawing a sun).
f. Cnidarians have nematocysts, or ________stinging cells__________ on their tentacles to grab
and sting their prey, then pull the food into their mouths.
g. Food, and oxygen go in the _______mouth__________ and waste and carbon dioxide go out the
_______mouth__________.
h. Cnidarians reproduce sexually with ____sperm_______ and _______egg_______ and
asexually by _______budding________.
Worm Phyla
a. The three worm phyla are _____flatworms________, ________roundworms___________,
and __________segmented worms_______________.
b. Flatworms are called _______Platyhelmenthesis____________________ and have a flat body, round
worms are called ____Nematoda_________________ and have a round body, and segmented worms
are called ____Annelida______ and have a round segmented (ringed)body.
c. An example of a flatworm is _______tapeworm, planaria_________, a round worm is
_trichinella, hockworm____, and a segmented worm is __earthworm, leech, feather dusterworm_.
d. Worms are made up of ___cells___________, _________tissues___________, and
_____organs__________, and segmented worms also have _____systems______.
e. Worms live in ______water________________, or _______land_________________.
f. Worms have __________bilateral___________ symmetry. Their right and left hand sides are
mirror images of each other.
g. Worms have two openings. Food comes in the ______mouth____________ and waste goes
out the _____anus_______________.
h. Worms breathe (oxygen in and carbon dioxide out) through ________moist skin______________.
If their skin dries out they will die.
i. Worms reproduce sexually with ______sperm____________ and _______egg____________.
Worm are hermaphroditic which means their bodies make both sperm and egg cells.
j. Worms can ____________regenerate_________________. If they are cut into half they will re-grow
the missing body parts.
k. Many worms are ______parasites___________. This means they feed off other living things for food.
Mollusk Phylum
a. The three mollusk classes are _________gastropod________, _________bivalve_____________,
and _________cephalopod______________________.
b. All mollusks have a mantle that makes a _______shell_______, a muscular foot, soft bodies,
a mouth and anus, and ______bilateral_________ symmetry.
c. Mollusks are made up of ______cells______________, _______tissues________,
______organs____________, and ________systems___________.
d. Gastropod mollusks, like _snail, slug, sea snail, neudrabranch_ have _1_ shell found on the outside of
their body (except all slugs with no shells). Gastropods move by __crawling___________ on
land or in water using their muscular stomach foot. They protect themselves by hiding in their shells or
with chemicals that _____taste bad______________.
e. Bivalve mollusks, like _clam, oyster, scallop, mussel_ have ___2_ shells found on the outside of
their bodies. They have a hatchet foot that allows them to dig themselves into the sand. Bivalves
don’t move far except for the ____scallop__________ that moves by clapping its shells
together. All bivalves live in ______water_________________. When sand
gets in one, it coats the sand with mucus until a ____pearl_______ is made. Bivalves are
_____filter_______ feeders and pull food and water in and across their gills. They protect
themselves by hiding in their shells and burying themselves in the sand.
f. Cephalopod mollusks, like _squid, octopus, nautilus, cuttlefish_ have ___1__ shell found on the inside
of their bodies except the octopus with no shell and nautilus with a shell on the outside. They have a
head foot that is broken up into ___tentacles_______________ that they use to move around and
capture food. Cephalopods can use _____jet propulsion__________ to move away from
predators very quickly. An octopus is able to change its body size, shape, and color to blend into its
surroundings. Many cephalopods also have ink to cloud up the water and let them escape. All
cephalopods live in ______water___________.
g. Mollusks reproduce sexually with ___sperm_________ and ______egg____________.
Mollusks are hermaphroditic which means their bodies make both sperm and egg cells.
Arthropod Phylum
a. The four arthropod classes are _____myriapod_______, _______crustacean____________,
________insect______________, and _______arachnid______________.
b. All arthropods have an ____exoskeleton___________ covering their body that they molt when it
gets too small for them, jointed appendages, segmented bodies, a mouth and anus, and __bilateral___
symmetry. Arthropods were the first to have separate ____genders______ and reproduce
sexually with sperm and egg. They also have a mandible (jaw) for chewing.
c. Arthropods are made up of _______cells__________, __________tissues___________,
_________organs_______, and _________systems_______.
d. Crustaceans, like _crabs, crayfish, lobster, shrimp, barnacles_ live in __water___ and breathe
with gills. They have five or more pair of walking legs and four or more pair of swimming legs.
Crustaceans have __2___ pair of antennae, __2____ body segments, and claws to grab
food with. The fiddler crab can regenerate its large front claw.
e. Myriapods, like _millipedes and centipedes_ live on ________land___________ and breathe
with air tubes. Myriapods have _1___ pair of antennae and many body segments. Centipedes have
__1____ pair of legs per segment and claws. They are poisonous. They are active hunters. Millipedes
have _2__ pair of legs per segment and are shy. They _curl up into a ball_ when afraid.
f. Most arachnid, like _spider, scorpion, tick, mite_ live on land and breathe with ___book lungs___.
The horseshoe crab lives in water and breathes with gills. Arachnids have _4____ pair of legs,
___no___ pair of antennae, and __2___ body segments. All spiders make silk but not all make
___webs_____. Scorpions have claws and poison in their ____tails_____. Ticks and mites are
_____parasites_______ and feed off other living animals.
g. Insects, like _bee, grasshopper, butterfly, ant, beetle_ live either in the air, land, or water and breathe
with ______air tubes_____. Insects have __3__ pair of legs, __1___ pair of antennae, and
__3__ body segments. Most insects have wings and can fly, and many have claws or stingers.
All insects go through either complete metamorphosis or incomplete (gradual) metamorphosis. The
stages of complete metamorphosis are egg, ___larva____, ______pupa_____, and adult. The
animal goes through a complete change while in the cocoon. The stages of incomplete metamorphosis
are egg, ____nymph____, and adult. The animal gradually, or slowly gets larger and larger as it
molts. During the last molt, it grows wings, changes body color, and its sexual organs begin to work.
Echinoderm Phylum
a. An example of an Echinoderm is a __starfish, sand dollar, sea urchin, feather duster, sea cucumber_.
b. All echinoderms live in __salt water (marine)______, many in tidal pools at beaches.
b. All echinoderms have __spiny_________ skin, a five part body, _____tube_______ feet,
a water vascular system to breathe and move with, and ____radial________ symmetry. They also
have a mouth and anus, and can ______regenerate_____ lost body parts. This allows them to
grow back what is missing or cut off.
c. Echinoderms are made up of _______cells_____________, ________tissues_____________,
_____organs____________, and _______systems____________.
d. Most Echinoderms use their ____tube feet________ to capture food and put it in their mouths.
Starfish eat by spitting their ____stomachs_____ out their mouths and digesting the mollusk in its
own shell. The sea cucumber can spit its intestines out its ____anus_______ to wrap up the
predator so the sea cucumber can crawl away.
f. Echinoderms reproduce sexually with ______sperm_________ and ____egg________________.
Invertebrates from simplest to most complex:
Porifera, Cnidarian, Platyhelmenthesis, Nematode, Mollusk, Annelid, Arthropod, Echinoderm.
Identifying%20invertebrates%20using%20a%20key%20-%20Questions
INVERTEBRATE PALEONTOLOGY GEOL4030 LECTURE 2 MICROFOSSILS TAXONOMY PROTHERO
INVERTEBRATE ZOOLOGY PROTISTA “DIVERSITY OF LIFE” MICROORGANISM THOMAS SOBAT
Tags: invertebrate phyla, invertebrate, notes, porifera, phyla, phylum
- LEGEA NR 2782020 DIN 27 NOIEMBRIE 2020 PENTRU APROBAREA
- ASIAN MONSOON PREDICTABILITY IN JMAMRI SEASONAL FORECAST SYSTEM TAMAKI
- PLAN DE TRABAJO 5º B (JUEVES 19032020) LENGUA
- PAPIROFLEXIA PARA CURRÍCULO ADAPTADO PREPARADO POR EZEQUIEL VEMOS FORMAS
- DR JOSEPH L KENNEDY PRESIDENT SUNY CANTON 34 CORNELL
- 4 INSTRUCTIONS FOR LIHEAP HOUSEHOLD REPORT FOR FFY 2020
- 7 OPGAVER TIL EL HOMBRE QUE VEIA DEMASIADO
- CURSO DE POSGRADO “TÓPICOS ACTUALES SOBRE METABOLITOS SECUNDARIOS EN
- S ISTEMAS DE COMUNICACIONES OPTICAS UDABOL RECEPTORES OPTICOS 1
- APPENDIX 1 BIOFOULING MANAGEMENT PLAN APPENDIX 1 BIOFOULING
- ENRIQUE J MOREA BORN APRIL 11 1924 BUENOS AIRES
- ACT ACCOUNTING POLICY ACCOUNTING FOR PROVISION FOR MAKE GOOD
- ANDRAGOŠKO UČILIŠTE ZVONIMIR ORGANIZIRA OSPOSOBLJAVANJE ZA POSLOVNE TAJNICE (TAJNIKE)
- Checklist to File an Unlawful Detainer Action Step one
- 1 MEMORIA DESCRIPTIVA DEL PROCEDIMIENTO A) DENOMINACIÓN DEL PROCEDIMIENTO
- APPENDIX G NONCOLLUSION AND NONSUSPENSION STATEMENT THE UNDERSIGNED CERTIFIES
- EL AYUNTAMIENTO DE ………………… SOLICITA ASESORAMIENTO SOBRE LA TRIBUTACIÓN
- TDS DUOMENŲ VITRINOS „APSKAITOS KORTELĖS DUOMENYS” NAUDOTOJO DOKUMENTACIJA DUOMENŲ
- PRÀCTICA 1 (EXERCICI 2) REGULARITZACIÓ DEL TEXT PRÀCTICA 1
- PISANIE POZIOM PODSTAWOWY KILKA DNI TEMU ZWYCIĘŻYŁEŚ(AŚ) W ZAWODACH
- IGLESIA CATÓLICA SAN ISIDRO STEDMAN NORTH CAROLINA REGISTRACIÓN FAMILIAR
- LAS LÁGRIMAS DE SHIVA DE CÉSAR MALLORQUÍ CAPÍTULO 2
- SC46 INF 13 (ENGLISH AND SPANISH ONLY ÚNICAMENTE
- A – TESTING DE LA FLEXION DU GENOU
- JAARVERSLAG OVER HET JAAR 2006 HET KLINKT AFGEZAAGD “DE
- CONTRACT OF LEASE THIS CONTRACT OF LEASE IS MADE
- MOVIMIENTOS POLITICOS TRANSITORIOS AÑO 2010 TRIBUNAL ELECTORAL DEL GUAIRA
- A GLOSSARY OF PARTICLE PHYSICS TERMS TERM DEFINITION ALICE
- ANUL II MG SERIA II GRUPA 7 PETRICALIA NOTA
- Anexo b Manual de Calidad Unidad Verificadora Código de
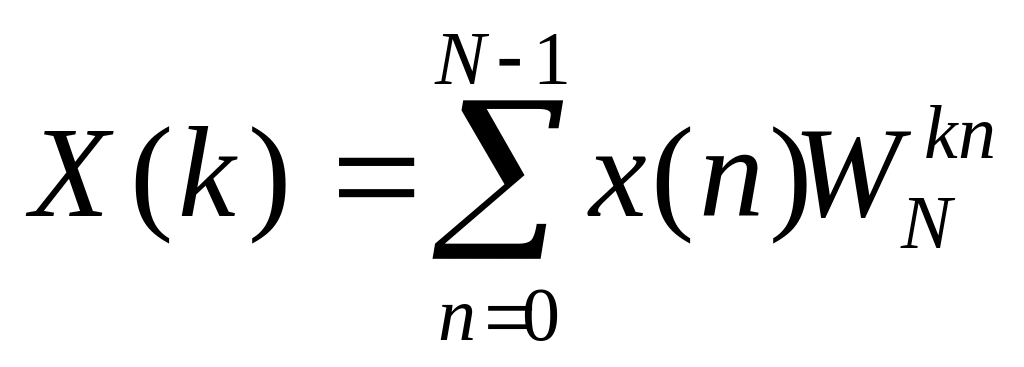 ĆWICZENIE NR 3 ROZKŁAD NA HARMONICZNE SYGNAŁÓW NIESINUSOIDALNYCH I
ĆWICZENIE NR 3 ROZKŁAD NA HARMONICZNE SYGNAŁÓW NIESINUSOIDALNYCH IPROJECT ANALYSIS & REVIEW “CAPACITACION EN OFICIOS BAJO
LIEPĀJAS PIRMSSKOLAS IZGLĪTĪBAS IESTĀDES ZĪĻUKS AMATPERSONAS ATALGOJUMS 2014GADS VĀRDSUZVĀRDS
BUSINESS ACADEMY DRESS GUIDELINES BUSINESS CASUAL IS A DESCRIPTION
 A PUNTES III 1 EL SUBJUNTIVO EL SUBJUNTIVO ES
A PUNTES III 1 EL SUBJUNTIVO EL SUBJUNTIVO ES CURRICULUM VITAE DATOS PERSONALES APELLIDOS DE LA MATA ALZINA
CURRICULUM VITAE DATOS PERSONALES APELLIDOS DE LA MATA ALZINAREGULAMIN KONKURSU PROMOCYJNEGO POD NAZWĄ „MOJE NAJPIĘKNIEJSZE ŚWIĘTA BOŻEGO
VO2 SS03 187107 INFORMATIK UND GESELLSCHAFT 1 WOLFGANG HOFKIRCHNER
 TYFLOCENTRUM PRAHA O P S KRAKOVSKÁ 21 110 00
TYFLOCENTRUM PRAHA O P S KRAKOVSKÁ 21 110 00 COMMONWEALTH OF PENNSYLVANIA CONTINUITY OF OPERATIONS PLAN TEMPLATE
COMMONWEALTH OF PENNSYLVANIA CONTINUITY OF OPERATIONS PLAN TEMPLATE DEKLARACJA POLITYKI UCZELNI ERASMUSA (STRATEGIA) PROSZĘ OPISAĆ STRATEGIĘ MIĘDZYNARODOWĄ
 INSPEKCJA WETERYNARYJNA POWIATOWY INSPEKTORAT WETERYNARII W LESZNIE UL ŚWIĘCIECHOWSKA
INSPEKCJA WETERYNARYJNA POWIATOWY INSPEKTORAT WETERYNARII W LESZNIE UL ŚWIĘCIECHOWSKAORGANIZAČNÍ A JEDNACÍ ŘÁD ČESKÉHO NÁRODNÍHO VÝBORU CTIF ČLÁNEK
NORMAS DE ESTÁGIO CURRICULAR NÃO OBRIGATÓRIO PARA MODALIDADES REMUNERADO
 BELOW YOULL FIND ANSWERS TO COMMON QUESTIONS ABOUT WISCONSIN’S
BELOW YOULL FIND ANSWERS TO COMMON QUESTIONS ABOUT WISCONSIN’SCIRCULAR 0182004 ASUNTO ACCESO A LA DOCUMENTACIÓN PROPIA DE
 ANGABEN ZUR EINSTUFUNG ALS KMU ANGABEN ZUR IDENTITÄT
ANGABEN ZUR EINSTUFUNG ALS KMU ANGABEN ZUR IDENTITÄTOM2015 PONUDA KONCESIONARA ZA UGOVARANJE SKUPNE PRAKSE ZA 2015
ANKIETA KANDYDATÓW NA RACHMISTRZÓW SPISOWYCH DO POWSZECHNEGO SPISU ROLNEGO
ZNAK SPRAWY 7TP2021 ZAŁĄCZNIK NR 7 DO SWZ ZOBOWIĄZANIE