BRAINSTORMING BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES OSBORN AF “THE ART OF CREATIVITY”
QUICK STUDY GUIDE 11 BRAINSTORMING & MIND MAPPINGACTIVITIES THAT MAKE TRAINING INTERACTIVE BRAINSTORMING – FREEWHEELING TECHNIQUE
BRAINSTORMING BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES OSBORN AF “THE ART OF CREATIVITY”
BRAINSTORMING ESSAY QUESTIONS COMPARISON AND CONTRAST (CC) – HOW
BRAINSTORMING GRID FOR REVIEWING A DANCE PERFORMANCE TO PROVE
BRIDGING THE DIGITAL DIVIDE REPORT ON THE BRAINSTORMING SESSION
VULNERABILITY ANALYSIS
BRAINSTORMING
Bibliographical references: Osborn A.F., “The art of creativity”, Milan, Franco Angeli, 1992, orig. ed. 1953.
Bertone V., “Business creativity. Methods, techniques; case studies to enhance the creative potential of managers and entrepreneurs.”, Milan, Franco Angeli, 1993.
Original title: Bertone V., “Creatività aziendale. Metodi, tecniche; casi per valorizzare il potenziale creativo di manager, imprenditori.”, Milano, Franco Angeli, 1993.
Cocco G.C., “Creativity research and innovation. Individuals and enterprises opposite the challenges of post-industrial society”, Milan, Franco Angeli, 1987.
Original title: Cocco G.C., “Creatività ricerca e innovazione. Individui e imprese di fronte alle sfide della società post-industriale, Milano, Franco Angeli, 1987.
Class: A
Phase: Idea generation, Internal mapping, Evaluation
Application field: All business processes in general; in particular New Product Development.
Assumptions: This technique could be applied individually but it should be better applied in group. The latter must be heterogeneous and free from inhibitions/restraints.
Pros: The technique does not need specific requirements and, in particular, the working group does not require preliminary training. A single session of brainstorming produces more good ideas than a traditional discussion, requiring short time.
Cons: Sometimes brainstorming sessions give only simple hints for future ideas, especially working with complex problems. Moreover, since these sessions are not structured, results may vary a lot depending on people involved.
Description:
The brainstorming technique was created by Alex Osborn in 1938. The term refers to the “disconnected thought” or “creative thought”. This tool asks people to leave their mind free to explore new ways, to invent new associations, to abandon old mental patterns. It is based on a group crossed discussion managed by a moderator. The brainstorming discussion provides a list of ideas, which should be used as a hint to solve a specific problem and which could be evaluated and elaborated subsequently.
This technique is based on the consideration that ideas refer to other ones, if they are expressed by different people. This process is metaphorically called cross-fertilization.
The process of brainstorming is very simple: when focusing on a specific problem this technique allows the group to create as many solutions as possible, as far as possible, without a pre-established order (see fig.1). The technique provides a great number of ideas and the linkages between them stimulate the generation of new proposals, in an auto-feeding process.
The most important thing which must be taken into consideration during the discussion is that each idea must be respected and must not be judged a priori.
The entire process is synthetizable in four main assumptions:
1. Deferred critical judgement
An idea should not be judged or evaluated at the same time in which it is generated. If the idea is judged, the one who produced it will try to protect it strongly instead of thinking about other possibly better ideas. The deferment of the assessment phase represents the most important feature of the brainstorming.
2. Unconventionality is welcome
Everyone should be stimulated to produce as much unconventional ideas as possible, without being worried to appear ridiculous. In this way everyone’s imagination can act freely.
3. Multiplication of ideas
Quantity rather than quality of ideas must be encouraged. They will be selected later.
4. Encourage the good ideas of other people
When several ideas are generated, everyone is encouraged to take into consideration and to modify other people’s ideas. This produces new ideas, better than the initial one.
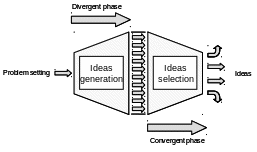
Fig.1. The generation of ideas in the brainstorming process.
The only strictly formal characteristic related with this technique is a written report of all the ideas generated. One or more people should write down each of these ideas, count them later on, without associating the name of the proponent. The list will be used as hints to find a solution for the considered problem.
The duration of a brainstorming session
An empirical rule suggests that the duration of a single brainstorming session should be approximately 30 minutes. If 30 minutes aren’t enough, it means that the problem have to be defined more clearly. If the group has only a short time for the session, then the ideas will probably be superficial.
The best achievable result using brainstorming technique is that, in each session, the group could generate much more good ideas (in a short time) than a traditional discussion. This technique improves creativity and initiative of the individuals.
Research studies demonstrate that this technique could be used both in individual and collective effort. An interesting and fruitful approach is to generate the core idea by yourself and, subsequently, to leave the development phase to the others. This kind of approach usually produces more ideas than the starting author could have done by himself.
Individual brainstorming
It generates a wider spectrum of ideas than the group’s session, but with less efficiency, because often individuals try to give thought to problems that they won’t be able to solve. On the other hand, individual could explore ideas in a better way, without being worried about wasting time or being criticized by someone else and, of course, without being dominated by the other members of the group.
Group brainstorming
It develops ideas more in depth than individual brainstorming. In fact, individual’s problems in developing ideas could be overcome by creativity and experience of somebody else.
Group brainstorming produces a smaller number of ideas (because time is used to develop ideas more in depth rather than to generate them) and moderate individuals could be repressed by the more noisy ones. In fact, in every group there are two different kind of people: on one hand there are intuitive/flexible people, on the other hand there are strict/logic people. The first category refers to creative thinkers, which are more fruitful in the initial phase. The second one refers to critical thinkers, which are useful in discussing about the feasibility of the generated ideas.
Combining individual and group brainstorming
Individual and group brainstorming could be combined together. For example, someone defines the problem individually and leaves the group free to find several superficial solution, if possible. Then, these solutions could be improved at individual level by specialists of each topic.
In any case, again as before, it is important to separate the idea’s generation phase from the assessment phase.
Operative rules for the brainstorming session
This section presents a couple of rules useful for a better direction of a brainstorming session. These rules are:
Someone must be asked to manage the session, to clearly define the problem and the objectives to achieve. It is important to leave the discussion free, without any kind of limitation.
This facilitator has to encourage an enthusiastic behaviour in the group, without criticism, and has to spur each participant to express his/her point of view. It is better to define the duration of the session from the beginning, while no topic has to be followed for much time. It is also better to focus the discussion on practical solutions of the problem.
The people attending brainstorming sessions should come from different disciplines, with a wide spectrum of experience, so as to obtain more creative ideas from the session.
People should be stimulated to do brainstorming in the most informal and amusing way, giving all possible ideas, from practical ones to those that are apparently unfeasible, generating a creative environment. All ideas will be accepted and registered.
Ideas must not be criticized or judged during the brainstorming session. In fact criticism could inhibit individuals to explain his/her own ideas. This behaviour kills creativity and yields ineffective sessions. It is easier to unwrap bad ideas at the end of the session, than generating good ones. At this point the question could be: “don’t you think this is a waste of time?”. The answer obviously is no, because these unfeasible ideas could stimulate the others to produce new original and innovative ideas.
It is advisable to encourage participants to work on other people’s ideas, in order to improve them.
Limitations of a brainstorming session
Besides positive aspects there are also some limitations of the brainstorming technique that must be taken into consideration. As observed by Osborn (1992), sometimes brainstorming sessions don’t produce results as expected, fundamentally for two main reasons:
faulty operation: lack of adhesion with procedures based on experience
overrated expectation: sometimes people forget that miracles do not happen that often.
In synthesis, the result of the brainstorming techniques are the following:
some sessions could produce effectively final answers, but only if the problem is easy…
some sessions could produce hints for further projects
some sessions could provide check-lists to promote new creative thoughts
some sessions could provide an approach to the following problem-solving phase. This is true especially when facing complex problems as technological ones.
Related techniques:
Besides the main brainstorming technique just described, it is possible to find several variants, even thought the basic rules of the process are the same. This techniques are:
UNREAL BRAINSTORMING
NEGATIVE BRAINSTORMING
RAWLINSON BRAINSTORMING
VALUE BRAINSTORMING
VISUAL BRAINSTORMING
BRAINWRITING
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING
TRIGGER SESSIONS- HIGHLIGHTING
CGIAR ICTKM PROGRAM—ONLINE LEARNING RESOURCES (OLR) PROJECT BRAINSTORMING WORKSHOP
ELEARNING LESSON DIFFRACTION AND INTERFERENCE OF MECHANICAL WAVES BRAINSTORMING
FORCES OF CHANGE BRAINSTORMING WORKSHEET THE FOLLOWING TWOPAGE WORKSHEET
Tags: bibliographical references:, osborn, creativity”, brainstorming, references, bibliographical
- 11 REGLAMENTO DE LA SECRETARIA GENERAL DE
- JILL ANNE CHOUINARD SCHOOL OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION UNIVERSITY OF
- UMOWA O OBJĘCIU ŚWIADCZENIAMI Z ZAKRESU MEDYCYNY PRACY POMIĘDZY
- PROCEDURE 524 INSURANCE INDEMNITY RESEARCH AGREEMENTS AND THE VMIA
- “LA INFORMACIÓN QUE CONSTA EN ESTE FORMULARIO SERÁ DE
- TEXTOS PARA COMENTAR TEMA 1 LA FILOSOFÍA Y EL
- CRCCSR1177 PAGE 11 NATIONS UNIES CRC CONVENTION
- APSTIPRINĀTS VIESĪTES NOVADA PAŠVALDĪBAS IEPIRKUMU KOMISIJAS 2017GADA 20 SEPTEMBRA
- PENGAJIAN KITAB IMAM SYAFII DI PESANTREN HUSNAYAIN SENIN 11
- REGULAMIN MUSZTRY 1 WSTEP MUSZTRA JEST JEDNYM Z ELEMENTÓW
- BESCHEINIGUNG ÜBER AUSGEÜBTE TÄTIGKEITEN NACH DEN BESTIMMUNGEN DER RICHTLINIEN
- ASSET MANAGEMENT PLAN WHILE A ‘FIXED ASSET REGISTER’ CONTAINS
- UNIVERSITY POLICY ON COURSES – AWARD CERTIFICATION SCHEDULE
- KAWARTHA PINE RIDGE DISTRICT SCHOOL BOARD – POLICY STATEMENT
- PLAN ZAJĘĆ DLA 2 ROKU I STOPNIA – KIERUNEK
- SE ADJUNTA INFORMACIÓN RECIBIDA DE LA EMBAJADA DE TURQUÍA
- MATERIALES PARA TRABAJAR LA EDUCACIÓN EN VALORES A PÁGINAS
- 92 SUMAS Y MÁS SUMAS EN GENERAL ES DIFÍCIL
- JUHTA JULKISEN HALLINNON TIETOHALLINNON NEUVOTTELUKUNTA JHS 106 POSTIOSOITE
- P ANEVROPSKI UNIVERZITET B A N J A L
- NORMAS DE PUBLICACIÓN SHORT PAPER TISE 2017 1ST AUTHOR
- ALLA SCOPERTA DEL DUOMO DI FIDENZA CON YOSHIE KOJIMA
- (IME I PREZIME) (ADRESA STANOVANJA) (KONTAKT
- INVESTIGATIVE QUESTION WHAT GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES OR BEDROCK PROPERTIES ARE
- KOMUNALNO DUGA RESA DOO DUGA RESA FINANCIJSKI IZVJEŠTAJ S
- ORGANİZASYONLARDA BİREYLER TUTUM DAVRANIŞ VE MOTİVASYON DOÇDR ÖZKAN TÜTÜNCÜ
- OBSAH PUBLIKACÍ 1 BOB CARR ENERGIE POTRAVIN 1992 2
- PREPARACIÓN DE TRABAJOS PARA EL I CONGRESO IBEROAMERICANO DE
- A UCZYNKI MIŁOSIERNE WOBEC CIAŁA 1 GŁODNYCH NAKARMIĆ 2
- PARLAMENTUL EUROPEAN 20142019 NODOCSE01272016NODOCSE DATE{30112016}12122016DATE TITRETYPEDECLARAȚIE SCRISĂTITRETYPE TITRERECUEILPREZENTATĂ ÎN
ARBEIDSLISTE SØMNAMESSA 2008 ONSDAG 15OKTOBER FØLGENDE MØTER KL
 ÜLLŐ VÁROS HUMÁN SZOLGÁLTATÓ KÖZPONT JELZŐRENDSZERES HÁZI SEGÍTSÉGNYÚJTÁS SZAKMAI
ÜLLŐ VÁROS HUMÁN SZOLGÁLTATÓ KÖZPONT JELZŐRENDSZERES HÁZI SEGÍTSÉGNYÚJTÁS SZAKMAI EXTENSIÓN PHUKET PHI PHI Y KOH SAMUI 4 DÍAS
EXTENSIÓN PHUKET PHI PHI Y KOH SAMUI 4 DÍAS UTARBEIDET AV DIETMAR WOLF SPORTSLIG LEDERUTDANNINGSKONSULENT I NSF 5
UTARBEIDET AV DIETMAR WOLF SPORTSLIG LEDERUTDANNINGSKONSULENT I NSF 5 GERENCIA DE COMUNICACIONES NOTA DE PRENSA N° 123 HASTA
GERENCIA DE COMUNICACIONES NOTA DE PRENSA N° 123 HASTA 4 D IVISIÓN DE CONTRATACION ADMINISTRATIVA Nº 07190 LEVPROH
4 D IVISIÓN DE CONTRATACION ADMINISTRATIVA Nº 07190 LEVPROHALLEGATO A INFORMATIVA EFFETTUATA AI SENSI DELL’ART 13 REGOLAMENTO
 NOTA SUCINTA SOBRE EL EXPEDIENTE DE CONCENTRACIÓN C011008 ABERTISAXIÓN
NOTA SUCINTA SOBRE EL EXPEDIENTE DE CONCENTRACIÓN C011008 ABERTISAXIÓN ST JOHN’S HELPER ST JOHN’S UNITED CHURCH OF CHRIST
ST JOHN’S HELPER ST JOHN’S UNITED CHURCH OF CHRIST GREEN FUTURES FROM UTOPIAN GRAND SCHEMES TO MICROPRACTICES ARBETETS
GREEN FUTURES FROM UTOPIAN GRAND SCHEMES TO MICROPRACTICES ARBETETSDNA FINGERPRINTING A SIMULATION NAMEPERIODTRAY DATE TEAM MEMBERS DUMAS05
 DISTRICT LAB PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES CONTENT OBJECTIVE STUDENTS
DISTRICT LAB PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES CONTENT OBJECTIVE STUDENTSMODEL DE CERERE PENTRU EMITEREA AVIZULUI COMISIEI TEHNICE DE
CONCLUSION SUR LE MEMBRE SUPÉRIEUR ILES ARTICULATIONS L’ARTICULATION
 UNIT ACTIVITY UNIT ADVANCED FUNCTIONS THIS ACTIVITY WILL HELP
UNIT ACTIVITY UNIT ADVANCED FUNCTIONS THIS ACTIVITY WILL HELPLESSON 1 WORKSHEET – INTRODUCTION TO PROVERBS STUDENT DATE
METODOLOGIA DE LA INVESTIGACION CUALITATIVA GREGORIO RODRÍGUEZ GÓMEZ JAVIER
PROTOKÓŁ NR XXVII09 RADY GMINY JELENIEWO Z DNIA 21
 [DATE] [NAME] [TITLE] [ORGANIZATION] [ADDRESS] [CITY STATE ZIP] 123
[DATE] [NAME] [TITLE] [ORGANIZATION] [ADDRESS] [CITY STATE ZIP] 123AUDIENCIA PROVINCIAL DE BIZKAIA BIZKAIKO PROBINTZIA‑AUZITEGIA SECCIÓN 1ª BARROETA