STROKE SYNDROMES MAIN SYMPTOM HEMIPARESIS (FACIOBRACHIOCRURAL WEAKNESS) ASSOCIATED SYMPTOMS
WHAT IS THE INTERNATIONAL STROKE PERFUSION IMAGING REGISTRY14 THE FOURSTROKECYCLE SPARKIGNITION (PETROL) ENGINE 1 INDUCTION STROKE
2 DECEMBER 2010 ARBETSTERAPIBITRÄDENS ROLL I STROKEVÅRDEN OBEROENDE AV
30072016 BASIN BÜLTENİ ONUR TELLİ STROKE PLAY’DE ŞAMPİYON ULUSLARARASI
40 WAYS TO LEARN PREWRITING STROKES AND LETTERSNUMBERS WITHOUT
A MOUSE MODEL OF POSTSTROKE PNEUMONIA INDUCED BY INTRATRACHEAL
Stroke Syndromes
|
Main symptom:
Hemiparesis (faciobrachiocrural weakness)
|
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• Cortical sensory loss, global aphasia or spatial neglect, hemianopsia, contralateral gaze palsy
|
• Middle cerebral artery (entire territory) syndrome |
|
|
• Hemisensory loss, transcortical motor or sensory aphasia |
• Middle cerebral artery (deep territory)
• Watershed infarct (between superficial and deep middle cerebral artery territory)
|
|
|
• Sensory loss (face and hand), conduction aphasia, apraxia, Gerstmann syndrome, constructional apraxia
|
• Perisylvian, superficial middle cerebral artery territory |
|
|
• Hemisensory loss, gaze palsy, spatial neglect, or expressive aphasia
|
• Middle cerebral artery, superior division (superficial territory) |
|
|
• Ipsilateral 3rd nerve palsy (Weber syndrome) +/- Supranuclear vertical gaze palsy +/- Sensory deficit
|
• Posterior
cerebral artery--paramedian midbrain perforators
|
|
|
• Ipsilateral 6th nerve palsy +/- 7th nerve palsy (Millard-Gubler syndrome), internuclear ophthalmoplegia, horizontal gaze palsy, one-and-a-half syndrome
|
• Basilar artery--paramedian pontine perforators |
|
|
• Ipsilateral 12th nerve palsy, contralateral loss of position and vibratory sense (medial medullary syndrome--Dejerine syndrome)
• Ipsilateral ataxia + Contralateral hemiparesis
• Ipsilateral ataxic hemiparesis
|
• Vertebral
artery, anterior spinal artery--paramedian medullary perforators
|
|
|
Facio-brachial weakness
|
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• Cognitive and behavioral abnormalities (abulia, agitation, hyperactivity, neglect) |
• Middle cerebral artery complete or lateral lenticulostriate territory
• Anterior
cerebral artery proximal perforating branches from Heubner artery
territory--caudate infarcts
|
|
|
Crural weakness |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms |
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• Homolateral ataxia
|
• Anterior cerebral artery distal territory |
|
|
• Noncortical sensory loss +/- Transcortical motor aphasia or mutism, mood disturbances
|
• Superficial borderzone territory between anterior and middle cerebral artery |
|
|
• Sensory loss, shoulder weakness, gegenhalten, left hand apraxia, alien hand sign, grasp reflex, transient urinary incontinence, abulia, akinetic mutism
|
• Anterior cerebral artery complete territory |
|
|
Brachial weakness |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• Cortical sensory loss, disturbance of volitional saccadic eye movements |
• Borderzone territory between anterior and middle cerebral artery
• Middle cerebral artery superficial territory: cortical infarct
|
|
|
Bilateral weakness - hemiparesis |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
+/- Sensory loss |
Internal carotid artery territory: • Bilateral hemispheric
Anterior spinal artery territory: • Bilateral medullary pyramids • Spinal cord infarction
|
|
|
• Locked-in syndrome +/- Supranuclear vertical gaze palsy |
Basilar artery territory: • Bilateral paramedian pontine or mesencephalic
|
|
|
Bilateral weakness - brachial weakness
|
||
|
|
Associated symptoms |
Anatomy & vascular territory
|
|
|
• Bilateral anterior watershed infarctions (man-in-a-barrel syndrome)
|
|
|
• Vertigo, distal amyotrophy |
• Anterior spinal artery watershed (“snake-eyes” infarction) (Pullicino 1994)
|
|
|
Bilateral weakness - paraplegia |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• Akinetic mutism, abulia, grasp, urinary incontinence
|
• Anterior cerebral artery bilateral |
|
|
• Sensory level, urinary incontinence
|
• Anterior spinal artery infarction |
|
|
Bilateral weakness - pseudobulbar palsy |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• Facio-pharyngo-glosso-masticatory diplegia with automatic-voluntary dissociation, spasmodic laughing or crying
|
• Middle cerebral artery bilateral opercular branches |
|
|
+ Pyramidal signs, intellectual impairment |
• Anterior choroidal artery: bilateral perforating branches
|
|
|
+ Pyramidal or cerebellar signs, lack of dementia
|
• Basilar artery paramedian branches |
|
|
Sensory strokes |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• Loss of position sense, impairment of 2-point discrimination, somatotopagnosia, agraphesthesia, astereognosis +/- Hemiparesis, hemianopsia, aphasia or hemineglect pseudothalamic parietal sensory syndrome
• Faciobrachiocrural elementary sensory loss
|
• Middle cerebral artery--parietal branches |
|
|
• Restricted acral sensory syndrome: cheiro(hand)-oral, cheiro-pedal, cheiro-oral-pedal syndrome |
• Middle cerebral artery
•Thalamogeniculate pedicle
• Basilar artery: deep perforating or medullary arteries
• Small strokes in lateral thalamus, pontine tegmentum, corona radiata, parietal cortex, midbrain.
|
|
|
• Hemianesthesia, transient hemiparesis, hemiataxia, thalamic astasia, choreoathetoid movements, thalamic hand, paroxysmal pain +/- Hemianopsia (Dejerine-Roussy syndrome)
|
• Thalamogeniculate territory, proximal posterior cerebral artery |
|
|
Cerebellar ataxia - limb ataxia, gait imbalance |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
+/- Lateropulsion, vertigo, nausea and vomiting, nystagmus, ocular tilt reaction, dysphonia and dysphagia, (nucleus ambiguous: IX, X, XI), ipsilateral facial thermalgesia (5th cranial nerve), Horner syndrome, contralateral thermalgesia of trunk and limbs (Wallenberg syndrome)
|
• Vertebral artery brainstem branches from vertebral artery occlusion |
|
|
Contralateral analgesia or thermalgesia +/- Vertigo, nausea, vomiting, horizontal nystagmus, dysarthria, Horner syndrome, 4th nerve palsy
+ 3rd nerve palsy
+ Hemichoreoathetosis (Benedikt syndrome)
|
• Superior cerebellar artery: cerebellar + midbrain tegmentum infarction territory |
|
|
Cerebellar ataxia |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
+/- Supranuclear vertical gaze palsy
+ Defective convergence or convergence-retraction nystagmus
|
• Basilar or posterior cerebral artery--P1--paramedian perforators |
|
|
+ Light-near dissociation (Parinaud syndrome)
|
• Dorsal rostral midbrain syndrome |
|
|
• Vertigo, tinnitus, ipsilateral hearing loss, dysarthria, Horner syndrome, peripheral 7th nerve palsy, facial hypesthesia, contralateral thermalgesia of the limbs and trunk
|
• Anterior inferior cerebellar artery--pontocerebellar infarction |
|
|
Ataxic hemiparesis |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
+/- Sensory symptoms +/- Dysarthria (dysarthria- clumsy-hand syndrome) |
• Thalamogeniculate or basilar artery or middle cerebral artery--lacunar infarctions in pons, thalamus, internal capsule, medulla
|
|
|
+ Aphasia |
• Middle
cerebral artery-parainsular
|
|
|
Visual symptoms - monocular blindness (amaurosis fugax) |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
+/- Contralateral variable motor and hemisensory deficit
|
• Internal carotid artery territory ischemia |
|
|
Visual symptoms - visual-field defects - sectoranopia |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• Wedge-shaped defect straddling the horizontal median, pointing towards fixation
|
• Posterior choroidal artery - lateral geniculate body infarction |
|
|
• Sector defects adjacent to the vertical meridian, sparing the zone around the horizontal meridian
|
• Anterior choroidal artery--lateral geniculate body infarction |
|
|
Visual symptoms - quadrantanopia (inferior noncongruent) |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
+ Optic ataxia, difficulty judging size, distance, movement
|
• Anterior, middle, or posterior cerebral artery--watershed infarction |
|
|
+/- Cortical hypesthesia, aphasia (anomia, transcortical sensory, receptive) |
• Middle or posterior cerebral artery superficial watershed, middle cerebral artery (parietal optic radiations)
|
|
|
Visual symptoms - quadrantanopia (inferior congruent) |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
|
• Posterior cerebral artery--upper bank calcarine fissure
|
|
|
Visual symptoms - quadrantanopia (superior noncongruent) |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
|
• Middle cerebral artery inferior division (temporal optic radiations)
|
|
|
Visual symptoms - quadrantanopia (superior congruent) |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
|
• Posterior cerebral artery--lower bank calcarine fissure
|
|
|
Visual symptoms - hemianopsia |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• Isolated, +/- hemiparesis, hemisensory loss, ataxia
|
• Anterior choroidal artery territory |
|
|
+ Hemiparesis, sensory loss, aphasia or neglect |
• Middle cerebral artery--optic radiation infarction
• Left middle cerebral artery
|
|
|
• Alexia without agraphia |
• Posterior cerebral artery territory (occipital, mediotemporal and callosal branches)
|
|
|
+ Cortical blindness (if bilateral- Anton syndrome), release hallucinations, agitated delirium or confusion, visual and color agnosia, + Simultanagnosia, ocular ataxia, ocular apraxia (Balint syndrome) |
• Posterior cerebral artery bilateral (lower bank of calcarine fissure)
• Middle or posterior cerebral artery watershed (upper bank of calcarine fissure)
• Posterior cerebral artery territory stroke
|
|
|
Visual symptoms - visual hallucinations |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• In the hemianoptic field, transient or persistent, simple or complex, nonstereotyped
|
• Posterior cerebral artery territory stroke |
|
|
• Complex, detailed, + inversion of the sleep-wake cycle (peduncular hallucinosis)
|
• Basilar artery or posterior cerebral artery, paramedian perforators |
|
|
Encephalopathic symptoms |
||
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
Anatomy & vascular territory |
|
• Agitated delirium, abnormal behavior
|
• Posterior or middle cerebral artery or basilar artery: paramedian midbrain and thalamus, hippocampus, fusiform and lingual gyri (top-of-the-basilar
|
|
|
• Cognitive impairment-decline in mentation |
• Posterior cerebral artery: occipital plus splenial or parahippocampal infarct (Park et al 2009)
• Pontine infarction
• Middle
cerebral artery territory—right temporal, inferior frontal,
and parietal lobe infarction
|
|
|
• Abulia, manic behavior |
• Medial
frontal lobe, caudate
nucleus (anterior cerebral artery territory)
|
|
ACUTE STROKE DATA ELEMENTS V NEMSIS & NONNEMSIS DATA
ACUTE STROKE ICP AUGUST 2013FINAL PATIENT’S NAME ADDRESS HOSPITAL
BALANCE PROBLEMS AFTER STROKE PROBLEMS WITH BALANCE ARE COMMON
Tags: (faciobrachiocrural weakness), (faciobrachiocrural, syndromes, stroke, associated, symptoms, weakness), hemiparesis, symptom
- PRÁCTICA 1 REALIZACIÓN DE EJEMPLOS DE SISTEMAS DE ESPERA
- PAGE 2 OF 2 FIELD MANUFACTURING REVISION OF MANUFACTURING
- UNIVERSIDADE DOS AÇORES ANO LECTIVO 20 DISCIPLINA 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
- GERPAN® 4RSRF60 TOEPASSINGSGEBIED EN VOORDELEN VOOR BEPAALDE CONSTRUCTIES
- TMMOB MİMARLAR ODASI MESLEKİ DAVRANIŞ KURALLARI YÖNETMELİĞİ (41DÖNEM OLAĞANÜSTÜ
- STRONA 3 Z 3 FORMULARZ F04 DO PW31 ZAŁĄCZNIK
- FORM IR37B (1) DECLARATION BY NONSINGAPORE SRS ACCOUNT HOLDER
- TC TRABZON ÜNİVERSİTESİ DERS MUAFİYETİ VE UYUM
- SERVICIO DE HABILITACIÓN Y SEGURIDAD SOCIAL CONSULTAS MÁS FRECUENTES
- 01001 CHAPTER 211 RULES FOR THE DISPOSAL OF ANIMAL
- TITLE DR FIRST NAME SANJAY LAST NAME MISRA PHOTOGRAPH
- IMPORTERS OF METAL SCRAP IN INDIA MADHU SUDAN METALS
- DDª CON NIF EN CALIDAD DE TITULAR
- EL ENDEREZAMIENTO DE LA DEMANDA PERMITIDO POR EL NUEVO
- FRENCH AMERICAN BACCALAUREAT WHAT IS THE FRENCHAMERICAN BACCALAURÉAT (BFA)?
- NA TEMELJU OPĆE UREDBE O ZAŠTITI PODATAKA (EU) 2016679
- AKER SYKEHUS NEDENSTÅENDE ER MENT Å SKULLE GI SVAR
- HUMEDALES ARTIFICIALES COMO ALTERNATIVA PARA MEJORAR LA
- OBRAZAC ZA RAZOTKRIVANJE INTELEKTUALNE KREACIJE POVJERLJIVO POVJERLJIVOST INFORMACIJE IZNESENE
- EJERCICIOS NOMENCLATURA (4) FÍSICA Y QUÍMICA 1º BAC IONES
- BIS SCIENCE AND SOCIETY COMMUNITY CHALLENGE GRANT SCHEME
- WORKING TOGETHER TO DRIVE EXCELLENCE IN CARE FOR
- ÖVERLÄMNING FRÅN EN SKOLFORM TILL EN ANNAN FRÅN GRUNDSKOLAN
- PAUTA ACTIVIDADES SEGMENTOS EN EJES CARTESIANOS DIBUJA EL
- DOC 127752DOC INPUT CONTRIBUTION MEETING ID ARC 25 TITLE
- WTMIN(03)ST6 PÁGINA 3 ORGANIZACIÓN MUNDIAL DEL COMERCIO WTMIN(03)ST6 11
- YORKSHIRE & HUMBER REGIONAL TRANSFUSION COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS FROM THE
- PAGE 2021 FAKULTAS FARMASI UNIVERSITAS AIRLANGGA 17 SEPTEMBER
- NEW MEMBER INDUCTION [CALL UP NEW MEMBER WITH ANY
- COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO PERSONNEL POLICIES AND PROCEDURES NO DATE
ANTALET POLISER KOMMER ATT ÖKA I EN ALDRIG TIDIGARE
5 TALLER SOBRE FIJACIÓN DIFERENCIADA DE PRECIOS
 FOR 20000331 NR 312 FORSKRIFT OM UTØVELSE AV FANGST
FOR 20000331 NR 312 FORSKRIFT OM UTØVELSE AV FANGSTINFORMACE PRO KOMUNIKACI S ODBOREM SOCIÁLNÍHO ZABEZPEČENÍ V ŽÁDOSTECH
PRESENCIA ESPAÑOLA EN IFLA Y EBLIDA PEDRO HÍPOLA FACULTAD
 ESTIMADOS ESTUDIANTES DADA LA CONTINGENCIA NACIONAL POR EL COVID19
ESTIMADOS ESTUDIANTES DADA LA CONTINGENCIA NACIONAL POR EL COVID19MECANICA CON ANIMACIONES HTTPWWWTECNOLOXIACOMMECANISMOS EXCELENTE PÁGINA DEL PROFESOR
ŁÓDŹ DNIA ……………………… (IMIĘ I NAZWISKO) ……………………………………………………… (STANOWISKO)
Individual Employment Agreement Parties 3 Commencement of Agreement 3
 RENEWABLE ENERGY MIX FOR EGYPT HANI EL NOKRASHY DRING
RENEWABLE ENERGY MIX FOR EGYPT HANI EL NOKRASHY DRINGBÀI 1 Ý NGHĨA VÀ LỢI ÍCH THIẾT THỰC
¿EXILIO O NEOESCLAVISMO? IDENTIDADES FRAGMENTADAS INMIGRACIÓN Y GÉNERO EN
FORMULARIO PARA LA SOLICITUD DE INFORMACIÓN RELLENE LOS CAMPOS
 REPRESENTACIONS TEMPORADA 20102011 ANGLÈS – ELS PASTORETS ADAPTACIÓ
REPRESENTACIONS TEMPORADA 20102011 ANGLÈS – ELS PASTORETS ADAPTACIÓ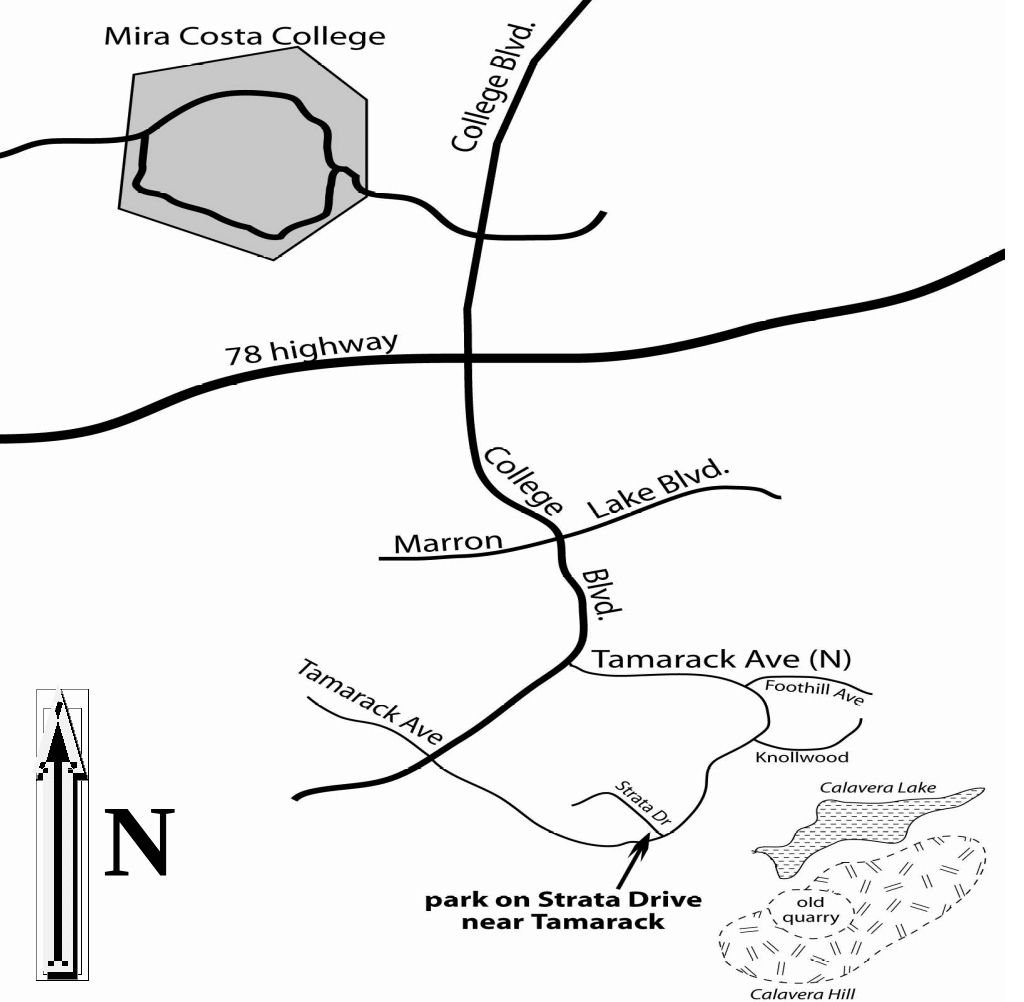 THE GEOLOGY OF CALAVERA HILLS NORTH SAN DIEGO COUNTY
THE GEOLOGY OF CALAVERA HILLS NORTH SAN DIEGO COUNTYKEJAKSAAN NEGERI KENDAL “UNTUK KEADILAN” S U R A
ZAŁĄCZNIK DO ZARZĄDZENIA KANCLERZA NR 1K12 UMOWA O PODNOSZENIU
GUYANA BILL NO 12 OF 2017 PROTECTED DISCLOSURES BILL
 ZÁZNAM O ÚRAZU SMRTELNÉM S HOSPITALIZACÍ DELŠÍ NEŽ 5
ZÁZNAM O ÚRAZU SMRTELNÉM S HOSPITALIZACÍ DELŠÍ NEŽ 5 ALFABETIZAR EL VOTO JOSÉ ADÁN RODRÍGUEZ CASTILLO “SEÑOR…AYÚDAME A
ALFABETIZAR EL VOTO JOSÉ ADÁN RODRÍGUEZ CASTILLO “SEÑOR…AYÚDAME A