MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQ) TOPIC QUIZ 51 RATES
MULTIPLE REGRESSION EXAMPLE CALIFORNIA RAINMIDDLESBROUGH COUNCIL LICENSING OF HOUSES IN MULTIPLE
1 MULTIPLE ALIGNMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL FUNCTIONAL OR PHYLOGENETIC ANALYSES
1 RANGKAIAN MULTIPLEXER 4X1 DENGAN MENGGUNAKAN STROBE ATAU ENABLE
12 MULTIPLE REGRESSION MODELS LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1 EXPLAIN
18 MODERATED MULTIPLE REGRESSION WORK NOTES AND SYNTAX VERSION
OCR A Level Chemistry A Multip(le Choice Question quiz (5.1 Rates, equilibrium and pH)

Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz
5.1 Rates, equilibrium and pH
Instructions and answers for teachers
These instructions cover the learner activity section which can be found on page 10. This Lesson Element supports OCR A Level Chemistry A.
When distributing the activity section to the learners either as a printed copy or as a Word file you will need to remove the teacher instructions section.
The Activity
This Lesson Element is a teaching and learning resource containing 10 multiple choice questions (MCQs) on the theme of rates, equilibrium and pH. Some questions might require synoptic thinking, using knowledge and ideas from various topics across the full A Level content.
This resource can be used to test and consolidate understanding at the end of a topic or to revisit and refresh knowledge at a later point in the course.
Learning Outcomes
This lesson element relates to the specification learning outcomes 5.1.1(b), 5.1.1(c), 5.1.1(d), 5.1.1(i), 5.1.1(k), 5.1.2(b), 5.1.2(f), 5.1.3(a), 5.1.3(g), 5.1.3(l)
Introduction
Multiple choice questions allow rapid coverage of a wide range of sub-topics.
Contrary to a widespread belief among students, multiple choice questions are not necessarily easy – they can be easy, moderate or difficult.
The questions are written so that the incorrect answers are plausible distractors based on common errors or misconceptions.
The questions in this quiz cover topics mainly from specification sections:
5.1 Rates, equilibrium and pH
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz – answers
Ka for ethanoic acid is 1.7 × 10–5 mol dm–3 at 25 °C.
What is the pH of a 0.125 mol dm–3
solution of ethanoic acid at this temperature?
-
A
0.75
They have treated is as a strong acid and got the calculation wrong, using 10–0.125
B
0.90
They have treated it as a strong acid, using –log 0.125.
C
2.8
Correct answer: pH = –log
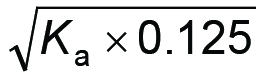
D
5.7
This is probably a guess, the calculation is –log(0.125 × 1.7 × 10–5)
C
A student monitors the rate of a reaction and plots the
concentration of one reactant against time. The shape of the
concentration–time graph is shown below.

What can be determined about this reaction?
-
A
The reaction is zero order with respect to this reactant.
The line would be straight, and the half-life would decrease
B
The reaction is first order with respect to this reactant.
Correct answer: The graph shows a downward curve with a constant half-life.
C
The reaction is second order with respect to this reactant.
The line would initially be steeper and half-life would increase
D
The rate of reaction is constant.
They may have noticed a constant half-life, but confused this with constant rate. The gradient of the graph becomes less steep over time, indicating a changing rate.
B
Carbon monoxide reacts with nitrogen dioxide:
CO(g) + NO2(g) CO2(g) + NO(g)
This reaction follows a two-step mechanism:
2NO2(g) NO3(g) + NO(g) Slow step
CO(g) + NO3(g) CO2(g) + NO2(g) Fast step
What is the correct rate equation for the reaction?
-
A
rate = k[CO][NO3]
They have based the rate equation on the fast step rather than the slow step.
B
rate = k[NO2]2[CO][NO3]
They have based the rate equation on the reactants of both the slow and the fast step, rather than just the slow step.
C
rate = k[NO2]2
Correct answer: The reactants in the slow step are two molecules of NO2.
D
rate = k[NO2]2[NO3][NO]
They have based the rate equation on all the species in the slow step, rather than just the reactants.
C
The Arrhenius equation k = Ae–Ea/RT can be rearranged so it can be represented by a straight-line graph.
Which expression represents the gradient of the graph?
-
A
–Ea/R
Correct answer: note that the linear expression is given on the Data Sheet.
B
ln A
This would be the value of the y-intercept, used to determine A.
C
ln k
This is plotted on the y-axis.
D
1/T
This is plotted on the x-axis.
A
A student mixes 6.0 mol of ethanoic acid and 12.5 mol of ethanol and allows an equilibrium to establish:
CH3COOH(l) + CH3CH2OH(l) CH3COOCH2CH3(l) + H2O(l)
At equilibrium 1 mol of ethanoic acid remains.
Which row gives the correct amounts of each substance at
equilibrium?
-
Amount (in mol) of substance
CH3COOH
C2H5OH
CH3COOCH2CH3
H2O
A
1
7.5
1
1
They have not realised that the amount of product increases as reactants are used up.
B
1
7.5
5
5
Correct answer.
C
1
12.5
5
1
They have connected the ethanoic acid reacted to the ester formed, but not thought through what happens to the other species.
D
1
12.5
5
5
They have not subtracted the 5 mol from the ethanol.
B
A mixture contains:
20 mol N2(g)
60 mol H2(g)
20 mol NH3(g)
The total pressure is 20 200 kPa.
What is the partial pressure of hydrogen?
-
A
336.7 kPa
They have just divided 20 200 kPa by the amount of H2.
B
1010 kPa
They have just divided 20 200 kPa by the amount of N2 or NH3.
C
4040 kPa
They have done the calculation for N2 or NH3 instead of H2.
D
12 120 kPa
Correct answer: The mole fraction of H2 is 60/100. 60/100 × 20 200 = 12 120.
D
Look at the reaction below.
H2NO3+ + H2SO4
![]() NO2+ + HSO4– +
H3O+
NO2+ + HSO4– +
H3O+
Which are a conjugate acid/base pair?
-
A
H2NO3+ and H3O+
Incorrect, they differ by more than one element.
B
H2NO3+ and HSO4–
Incorrect, they differ by more than one element.
C
H2SO4 and HSO4–
Correct answer: They differ by H+.
D
H2SO4 and H3O+
Incorrect, they differ by more than one element.
C
The following reaction is analysed to determine the order of reaction for each reactant.
BrO3–(aq) + 6I–(aq)
+ 6H+
3I2(aq) +
3H2O(l) + Br–(aq)
|
Experiment |
[BrO3–(aq)] / mol dm–3 |
[I–(aq)] / mol dm–3 |
[H+(aq)] / mol dm–3 |
Initial rate / mol dm–3 s–1 |
|
1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
4.8 × 10–3 |
|
2 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
4.8 × 10–3 |
|
3 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
0.2 |
9.6 × 10–3 |
|
4 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
1.9 × 10–2 |
What are the value and units of the rate constant?
-
A
0.48 dm3 mol–1 s–1
They have probably used order 1 for I–, looking at the change in rate from experiment 3 to experiment 4 but not taking into account [H+(aq)].
B
0.48 dm9 mol–3 s–1
Possibly a guess, the units do not match the calculation.
C
4.8 dm–6 mol2 s–1
The calculation is correct but they have determined the units incorrectly.
D
4.8 dm6 mol–2 s–1
Correct answer
D
Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, has a Ka of 1.7 × 10–5 mol dm–3. It can form a buffer solution when mixed with NaOH.
A student mixes equal amounts of solutions of CH3COOH and NaOH.
Which mixture will give a buffer with pH = 4.77?
-
[CH3COOH] / mol dm–3
[NaOH] / mol dm–3
A
0.1
0.2
This would not form a buffer as the base is in excess – the pH would be >7.
B
0.1
0.1
This would not form a buffer as the weak acid would be neutralised. The pH would be 7.
C
0.2
0.1
Correct answer: –log(1.7 × 10–5 × (0.2 – 0.1)/0.1)
D
0.3
0.1
Incorrect, this mixture would give a pH of 4.46.
C
Which of these statements is/are true for the Haber process?
N2 + 3H2
![]() 2NH3 H
= −92.4 kJ mol–1
2NH3 H
= −92.4 kJ mol–1
-
1
Increasing the temperature will increase the value of Kc.
2
Increasing the concentration of nitrogen will not change the value of Kc at equilibrium.
3
An iron catalyst will not affect the value of Kc.
A
1, 2 and 3
They may have mistaken the reaction for being endothermic.
B
only 1 and 2
They are possibly confusing equilibrium constant with rate constant, for which this combination would be correct.
C
only 2 and 3
Correct answer: Increasing the temperature will cause the equilibrium to shift towards the left, giving a small Kc. The value of Kc is not affected by concentration or presence of catalyst.
D
only 1
Incorrect, possibly a guess or combination of errors.
C
We’d
like to know your view on the resources we produce. By clicking on
‘Like’
or ‘Dislike’
you can help us to ensure that our resources work for you. When the
email template pops up please add additional comments if you wish
and then just click ‘Send’. Thank you.
If you
do not currently offer this OCR qualification but would like to do
so, please complete the Expression of Interest Form which can be
found here: www.ocr.org.uk/expression-of-interest
This
formative assessment resource has been produced as part of our free
Chemistry teaching and learning support package. All the Chemistry
teaching and learning resources, including delivery guides, topic
exploration packs, lesson elements and more are available on the
qualification webpages.
If you
are looking for examination practice materials, you can find Sample
Assessment Materials (SAMs) and a link to the Practice Papers on the
qualification webpages: Chemistry
A,
Chemistry
B.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz
5.1 Rates, equilibrium and pH
Learner Activity
Ka for ethanoic acid is 1.7 × 10–5 mol dm–3 at 25 °C.
What is the pH of a 0.125 mol dm–3
solution of ethanoic acid at this temperature?
-
A
0.75
B
0.90
C
2.8
D
5.7
A student monitors the rate of a reaction and plots the
concentration of one reactant against time. The shape of the
concentration–time graph is shown below.

What can be determined about this reaction?
-
A
The reaction is zero order with respect to this reactant.
B
The reaction is first order with respect to this reactant.
C
The reaction is second order with respect to this reactant.
D
The rate of reaction is constant.
Carbon monoxide reacts with nitrogen dioxide:
CO(g) + NO2(g) CO2(g) + NO(g)
This reaction follows a two-step mechanism:
2NO2(g) NO3(g) + NO(g) Slow step
CO(g) + NO3(g) CO2(g) + NO2(g) Fast step
What is the correct rate equation for the reaction?
-
A
rate = k[CO][NO3]
B
rate = k[NO2]2[CO][NO3]
C
rate = k[NO2]2
D
rate = k[NO2]2[NO3][NO]
The Arrhenius equation k = Ae–Ea/RT can be rearranged so it can be represented by a straight-line graph.
Which expression represents the gradient of the graph?
-
A
–Ea/R
B
ln A
C
ln k
D
1/T
A student mixes 6.0 mol of ethanoic acid and 12.5 mol of ethanol and allows an equilibrium to establish:
CH3COOH(l) + CH3CH2OH(l) CH3COOCH2CH3(l) + H2O(l)
At equilibrium 1 mol of ethanoic acid remains.
Which row gives the correct amounts of each substance at
equilibrium?
-
Amount (in mol) of substance
CH3COOH
C2H5OH
CH3COOCH2CH3
H2O
A
1
7.5
1
1
B
1
7.5
5
5
C
1
12.5
5
1
D
1
12.5
5
5
A mixture contains:
20 mol N2(g)
60 mol H2(g)
20 mol NH3(g)
The total pressure is 20 200 kPa.
What is the partial pressure of hydrogen?
-
A
336.7 kPa
B
1010 kPa
C
4040 kPa
D
12 120 kPa
Look at the reaction below.
H2NO3+ + H2SO4
![]() NO2+ + HSO4– +
H3O+
NO2+ + HSO4– +
H3O+
Which are a conjugate acid/base pair?
-
A
H2NO3+ and H3O+
B
H2NO3+ and HSO4–
C
H2SO4 and HSO4–
D
H2SO4 and H3O+
The following reaction is analysed to determine the order of reaction for each reactant.
BrO3–(aq) + 6I–(aq)
+ 6H+
3I2(aq) +
3H2O(l) + Br–(aq)
|
Experiment |
[BrO3–(aq)] / mol dm–3 |
[I–(aq)] / mol dm–3 |
[H+(aq)] / mol dm–3 |
Initial rate / mol dm–3 s–1 |
|
1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
4.8 × 10–3 |
|
2 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
4.8 × 10–3 |
|
3 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
0.2 |
9.6 × 10–3 |
|
4 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
1.9 × 10–2 |
What are the value and units of the rate constant?
-
A
0.48 dm3 mol–1 s–1
B
0.48 dm9 mol–3 s–1
C
4.8 dm–6 mol2 s–1
D
4.8 dm6 mol–2 s–1
Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, has a Ka of 1.7 × 10–5 mol dm–3. It can form a buffer solution when mixed with NaOH.
A student mixes equal amounts of solutions of CH3COOH and NaOH.
Which mixture will give a buffer with pH = 4.77?
-
[CH3COOH] / mol dm–3
[NaOH] / mol dm–3
A
0.1
0.2
B
0.1
0.1
C
0.2
0.1
D
0.3
0.1
Which of these statements is/are true for the Haber process?
N2 + 3H2
![]() 2NH3 H
= −92.4 kJ mol–1
2NH3 H
= −92.4 kJ mol–1
-
1
Increasing the temperature will increase the value of Kc.
2
Increasing the concentration of nitrogen will not change the value of Kc at equilibrium.
3
An iron catalyst will not affect the value of Kc.
A
1, 2 and 3
B
only 1 and 2
C
only 2 and 3
D
only 1
Version 1
1984 ADVANCED PLACEMENT EXAM PART I MULTIPLE CHOICE NOTE
3 PRACTICE QUIZ 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1
39 CHAPTER 9 EARNINGS MULTIPLES EARNINGS MULTIPLES REMAIN
Tags: (mcq) topic, questions (mcq), multiple, (mcq), questions, choice, topic, rates
- INTEROFFICE MEMORANDUM TO MICHAEL MCGOVERN TOWN MANAGER FROM MATTHEW
- ANEXA NR 6 LA SCHEMA DE AJUTOR DE MINIMIS
- SEMMELWEIS EGYETEM DOKTORI ISKOLA 14 MELLÉKLET SEMMELWEIS EGYETEM INTÉZMÉNYI
- MATH 400 THEORY OF INTEREST NAME HOMEWORK 18
- OP DE DIENSTEN VAN KINDEROPVANG MINI STEK ZIJN ZOWEL
- TÉRMINOS Y CONDICIONES (JULIO DE 2007) HA OPTADO USTED
- KARTA INFORMACYJNA PRACODAWCY ZATRUDNIAJĄCEGO MŁODOCIANEGO PRACOWNIKA W CELU PRZYGOTOWANIA
- DLINE 1 ISTRIBUIDORES DE PRODUCTOS ESPAÑOLES EN ESCOCIA DISTRIBUIDORES
- TRAVEL FORMS DESCRIPTIONS CLICK ON THE HYPERLINK TO
- IMPACT OF MATERIAL SURFACE PROPERTIES ON BUILDING PERFORMANCE ACROSS
- DEPARTAMENTO DEPARTAMENTO DEBIDO A LA SITUACIÓN ACTUAL Y PARA
- CLINICAL SITE INFORMATION FORM (CSIF) APTA DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL
- U NIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DE EDUCACIÓN A DISTANCIA ( UNED)
- T EMPORARY STORAGE CONTAINER INFORMATION SHEET THIS INFORMATION
- RESSOURCES WEBÉMISSIONS FAIRE CROÎTRE LE SUCCÈS L’ÉVALUATION AU
- SAĞLIK TURİZMİNE ENTEGRASYON VE THTC 7GENEL KURUL TOPLANTISI 25
- MODELLO ISTANZA DEPOSITO CIS – PRATICHE ART35 LEGGE 4785
- BÚSQUEDA DE EMPLEO 20 1 CANALES DE BÚSQUEDA
- HISTORIA DE LA CIUDAD DE NUEVA YORK DEL SISTEMA
- RESEARCH AGENDA FOR PREVENTING MOSQUITO TRANSMITTED DISEASES BY IMPROVING
- LAMPIRAN 5 KEPUTUSAN GUBERNUR BUPATI WALIKOTA ………………
- GDYNIA DNIA 29062018 R OGŁOSZENIE O ROZSTRZYGNIĘCIU KONKURSU OFERT
- VIII PHỤ LỤC 31 QUY ĐỊNH VỀ HÌNH
- MIDTVEISOPPGAVE I DOKTORGRADSPROGRAMMET PROSJEKT KANDIDAT HOVEDVEILEDER MEDVEILEDER 1 MEDVEILEDER
- ZASADY REALIZACJI ZAJĘĆ Z PRZEDMIOTU JĘZYK OBCY W
- NOVIEMBRE 2014 AGENDA DE ACTIVIDAD ASESORÍA ESPECIALIZADA PARA REVISIÓN
- CONSEGUIR TRABAJO EN ALEMANIA SITIOS WEB ÚTILES PARA ENCONTRAR
- FEDERAL OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH A COMPONENT OF THE US PUBLIC
- FECHA DE RECEPCIÓN (DATE RECEIVED) DOCUMENTO DE SOLICITUD DE
- MATEMÁTICA 2° MEDIO UNIDAD 2 OA3
 PROGRAM SPORTOWY 1 PROGRAM SPORTOWY WSG TO SYSTEM WSPIERAJĄCY
PROGRAM SPORTOWY 1 PROGRAM SPORTOWY WSG TO SYSTEM WSPIERAJĄCY NACIONES UNIDAS ALTO COMISIONADO PARA LOS DERECHOS HUMANOS OFICINA
NACIONES UNIDAS ALTO COMISIONADO PARA LOS DERECHOS HUMANOS OFICINA ARBEITSBLATT 6 BESEN BINDEN WIE VOR 100 JAHREN DIE
ARBEITSBLATT 6 BESEN BINDEN WIE VOR 100 JAHREN DIE 1949 – 2019 70 AÑOS DE LA GRATUIDAD UNIVERSITARIA
1949 – 2019 70 AÑOS DE LA GRATUIDAD UNIVERSITARIAGM LOOKS TO HAWAII FOR HYDROGEN INFRASTRUCTURE PILOT COLLABORATION
ÅRSMØTE I NAMDAL FUGLEHUNDKLUBB NAMSOS 9 MARS 2016 KL
INSTRUKCJA WYPEŁNIANIA FORMULARZA ZAP 3 1 AKTUALIZUJĄC MIEJSCE ZAMIESZKANIA
DECLARACIÓN UNIVERSAL DE LOS DERECHOS HUMANOS APROBADA POR LA
OZNACZENIE SPRAWY PN0311W SPECYFIKACJA ISTOTNYCH WARUNKÓW ZAMÓWIENIA NA SKŁAD
SPELPROGRAM SAMMANDRAG FLICKOR 01 I RYDEBÄCKS IDROTTSHALL LÖRDAGEN DEN
 KÖZSZERSZERVEZÉSI ÉS SZAKIGAZGATÁSI INTÉZET TANMENET ÉS TANTÁRGYI KÖVETELMÉNYEK A
KÖZSZERSZERVEZÉSI ÉS SZAKIGAZGATÁSI INTÉZET TANMENET ÉS TANTÁRGYI KÖVETELMÉNYEK A T C BANDIRMA ONYEDİ EYLÜL ÜNİVERSİTESİ SOSYAL BİLİMLER ENSTİTÜSÜ
T C BANDIRMA ONYEDİ EYLÜL ÜNİVERSİTESİ SOSYAL BİLİMLER ENSTİTÜSÜHOSPITAL INCIDENT COMMAND EXERCISE EVALUATION GUIDE CAPABILITY DESCRIPTION HOSPITAL
 FACT SHEET ON THE IASC GENDER MARKER 1 WHY
FACT SHEET ON THE IASC GENDER MARKER 1 WHYMODELO 3 CEIP LUCIEN BRIET DESDE EL CEIP LUCIEN
 CITY OF TULSA GRANTS ADMINISTRATION (GA) CDBG MONTHLY
CITY OF TULSA GRANTS ADMINISTRATION (GA) CDBG MONTHLYCBDUNFCCCUNCCD INTEROPERABILITY FUNCTIONAL SPECICFICATIONS CBDUNFCCCUNCCD INTEROPERABILITY FUNCTIONAL SPECIFICATIONS REVISED
 EK3 PROJE TANIMLAMA DOKÜMANI (PTD) ŞABLONU OPERATION IDENTIFICATION
EK3 PROJE TANIMLAMA DOKÜMANI (PTD) ŞABLONU OPERATION IDENTIFICATION 29 CRISTO FLAGELADO CRISTO CRUCIFICADO MÍSTICA DE LA SANGRE
29 CRISTO FLAGELADO CRISTO CRUCIFICADO MÍSTICA DE LA SANGRE UNIVERSIDAD DE CHILE FACULTAD DE CIENCIAS SOCIALES ESCUELA DE
UNIVERSIDAD DE CHILE FACULTAD DE CIENCIAS SOCIALES ESCUELA DE