NAME MARIANNE DUER ALVAREZ DATE 21712 STUDENT EXPLORATION READING
DOMAINSTANDARD CODE KCC1 AUTHOR NAME MARIANNE JODI DEBBIE JULIEJURISPRUDENTIE RAAD VAN STATE BETREFFENDE WATER EN WATERTOETS MARIANNE
NAME MARIANNE DUER ALVAREZ DATE 21712 STUDENT EXPLORATION READING
NOTAT MARIANNE AARS PR 8 JANUAR 2014 1 HVORFOR
PARA LO QUE ESTAMOS MARIANNE PONSFORD EL ESPECTADOR DOMINGO
PROF DR MARIANNE HEIMBACHSTEINS SIECHENSTRASSE 53 96052 BAMBERG PUBLIKATIONSLISTE
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
Name: _Marianne Duer Alvarez_ Date: _2/17/12_
Student Exploration: Reading Topographic Maps
Vocabulary: contour interval, contour line, depression contour, elevation, gradient, index contour, relief, topographic map
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
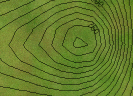
A house sits on the side of a small hill near a lake. The elevation, or height, of each point above the lake is shown by the contour lines on the landscape below.

Suppose it rained for a while, and the lake level rose up 5 meters. Would the house be safe? Explain.
_Yes because the house is between the 5 m mark and the 10 m mark_
What would happen if the lake level rose 10 meters?
_The house would be under sea level_
Gizmo Warm-up
A topographic map is a map that contains contour lines to show elevation. Each contour line connects points that are at the same elevation. The Reading Topographic Maps Gizmo™ allows you to see how a three-dimensional landscape can be represented by a two-dimensional map.
The controls at the top of the Gizmo allow you to manipulate the landscape on the left and the map on the right. Try each tool:
With the Rotate tool selected, click and drag to turn the map or landscape.
Select Zoom In and click the landscape several times. Then select Zoom Out and click the landscape again to return it to its original size.
Click the Add button, and then click several times on the landscape or map to add a hill. Then dig a hole using the Subtract tool.
Enter a new Interval using your keyboard. The contour interval is the elevation change between contour lines.
Now use the slider to change the Water level. Look out for a flood!
Try the remaining tools and buttons on your own.
|
Activity A:
Contour lines |
Get the Gizmo ready: Click Flat to start with a flat landscape. Set the Interval to 50 m. Set the Water level to 0 m. |
|
Question: How do contour lines indicate elevation?
Observe: Select Add, and then click in the center of the landscape exactly four times. Click Horizontal View and use the Zoom In tool to magnify the landscape.
What feature have you created? _mountain_
Look at each contour line on the horizontal view at left. What do you notice?
_They are stacked up, and go all the way around the mountain_
Calculate: Notice that one contour line is labeled with an elevation. This is an index contour. The elevation is given in meters above sea level. Because the contour interval is 50 meters, each line above the index contour represents an elevation gain of 50 meters.
What is the elevation of the highest contour line on the hill? _350 m_
What is the elevation of the lowest contour line you can see? _50 m_
What is the maximum height the hill could be? Explain. _350 m because that’s the highest elevation in the hill_
Raise the Water level until the water is just at the top of the hill. To the nearest 10 meters, what is the actual elevation of the hill? _600 m_
Create: Reduce the Water level to 0 m, and click Flat. Select the Subtract button and click the center of the landscape exactly three times. Choose the Isometric view.
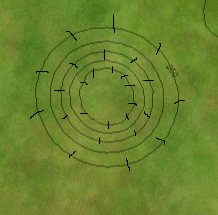
What feature have you created? _a depression_
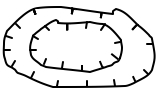
In real topographic maps, depression contours are indicated by hachure marks, shown at right.
Based on the contour lines, what is the lowest possible elevation of the deepest point in the depression? _-250_
Check with the Water level slider. What is the lowest elevation? _-250 m_
|
Activity B:
Slope |
Get the Gizmo ready: Click Flat. Select the Horizontal View. |
|
Question: How do contour lines indicate steepness?
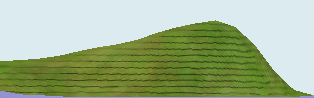
Create: Use the Add and Subtract tools to create an asymmetrical mountain similar to the one shown at right. The right side of the mountain should be steep, and the left side of the mountain should be gentle.
Compare the landscape to the map. How does the spacing of contour lines relate to the steepness of the mountainside? _the skinnier the space is, the steeper the mountain is_
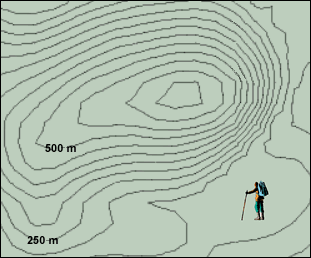
Apply: A hiker wants to climb a mountain. He is afraid of slopes that are too steep, however.
On the map, draw the gentlest route from the hiker to the top of the mountain.
What is the contour interval of this map?
_50 m_
What is the maximum possible elevation of the mountain? _650 m_
Calculate: The gradient of a mountainside is a measure of its steepness. Like the slope of a graph, gradient is calculated by dividing the vertical rise by the horizontal distance, or run. Because meters are divided by meters, there are no units for gradient.
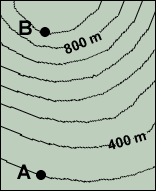
What is the contour interval of the map at left? _80 m_
What is the elevation of point A? _320 m_
What is the elevation of point B? _880 m_
What is the elevation change between A and B? _480 m_
If
the horizontal distance between point A
and point B
is
2,800 m, what is the gradient? _0.17143_
|
Activity C:
Interpreting maps |
Get the Gizmo ready: Click New. |
|
Question: How do we interpret contour maps?
Observe: Look at the landscape and the corresponding topographic map. Then use the Add and Subtract tools to create each of the following features: a hill, a depression, a ridge, and a valley. Sketch the contour lines that represent each feature in the boxes below. (Note: Don’t forget to put hachure marks on the depression contour lines.)
|
Hill |
Depression |
|
Ridge |
Valley |
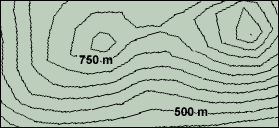
Calculate: The relief of a contour map is the difference between its highest and lowest points.
What is the estimated relief of this map? _250 m_
Practice: Click COPY SCREEN at the bottom right to take a screenshot of the Gizmo. Open a blank document, and paste in the screenshot. Click New, and repeat this until you have at least 4 maps. Print your document.
For each map in your document, label or state the following:
The tallest point on the map and its estimated elevation.
The lowest point on the map and its estimated elevation.
The relief of the map.
The steepest slope on the map.
A gentle slope on the map.
In addition, label any hills, ridges, valleys, or depressions that you see. You can name the mountains, valleys, and other features if you like!
![]()
PUBLICATIONS PRINCIPALES DE MARIANNE BASTIDBRUGUIÈRE CONTRIBUTIONS À DES OUVRAGES
THE CYBER BULLY BY MARIANNE T VERNACCHIA MFT CLINICAL
UNCLASSIFIED REMARKS BY HE MRS MARIANNE YOUNG BRITISH HIGH
Tags: reading, student, 21712, exploration, marianne, alvarez
- UND GENERAL SURGICAL RESIDENCY PROGRAM COMPETENCY BASED PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
- 1 CORE DETAILS A PPLICATION FOR AUTHORISATION APPLICATION FORM
- CREAR CARPETAS EXISTEN VARIAS FORMAS DE CREAR CARPETAS NOSOTROS
- PROGRAMA DE ACTIVIDADES WHAT´S ON IN ESTEPONA JULIO
- STATEMENT OF PRINCIPLES CONCERNING LABRAL TEAR NO 94 OF
- DIPLOMATURA DE ESTUDIOS EN AGENTES INMOBILIARIOS (DEAI PUCP) 19
- PRODUCER POSTPRELIMINARY PROCESSING WORK INSTRUCTION PURPOSE THE PURPOSE IS
- Responsabilidad Medica Intervención Quirúrgica Hipoacusia Implante Auditivo Secuelas Irreversibles
- ESTADO DE GOIÁS GOVERNO DA CIDADE DE MORRINHOS ASSESSORIA
- 0 (R C DE LA C 2013) RESOLUCION CONJUNTA
- WTDS35018ADD26 PÁGINA 0 ORGANIZACIÓN MUNDIAL DEL COMERCIO WTDS35018ADD26 10
- CONSEIL COMMUNAL DU 27102020 CONSEIL COMMUNAL DU 27102020 COMPTE
- PART 1 FISCAL YEAR 2015 REPORTING SUPPLEMENT SECTION III
- MAGD STUDY PROGRAMS LISTED BELOW ARE MASTERSHIP STUDY
- CONFÉRENCE INTERNATIONALE « LEUR DETTE NOTRE DÉMOCRATIE » PARIS
- CHANGE OF ADDRESS LINK ASSET SERVICES THE REGISTRY 34
- ANALISIS STANDAR JUMLAH PERSONEL PENANGANAN PENGANGKUTAN BARANG BERBAHAYA DI
- CONGRESO LATINOAMERICANO Y CARIBEÑO DE CIENCIAS SOCIALES –FLACSO 50
- 3513 DESIGN SUMMARY TABLES FOR EROSION AND SEDIMENT CONTROL
- D4 – GUIDELINES 2015 GUIDELINES ON THE LAYOUT
- LOKALNE VOLITVE 2018 INSTRUKTIVNI OBRAZEC SOGLASJE KANDIDATA ZA MESTNEGA
- PERF14B ENCUESTA VALORACIÓN PLAN CANARIO DE FORMACIÓN
- ESTER REBOLLO 71 C OPIA Y RELACIONA PUPA ……………
- VUELTAS NOCTURNAS O EXPERIENCIAS SEXUALES DE
- NACRT U G O V O RA O DODJELI
- ANEXO MEMORIA A DADES DEL SOL·LICITANT DATOS DEL
- EL JOVEN DE CANADÁ TRABAJA (YOUNG CANADA WORKS) CANADÁ
- SUBDIRECCIÓN GENERAL DE ESTUDIOS Y DOCTRINA SUBDIRECTOR GENERAL DE
- ABSTRACT OF LECTURE HERMANN CZECH BUILDINGS ARE TIME MACHINES
- SENSITIVE TEETH Q WHAT ARE SENSITIVE TEETH?
 INFORME PARA EL INTERCAMBIO DE INFORMACIÓN SOBRE CASOS RELACIONADOS
INFORME PARA EL INTERCAMBIO DE INFORMACIÓN SOBRE CASOS RELACIONADOS REGULARLY SCHEDULED CONFERENCE LETTER OF AGREEMENT TO BE IN
REGULARLY SCHEDULED CONFERENCE LETTER OF AGREEMENT TO BE IN7192007 M2612 ABOUT THIS MANUAL ABOUT THIS MANUAL INTRODUCTION
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ РЕСПУБЛИКИ БЕЛАРУСЬ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ «БРЕСТСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ
 CURSO DE APTITUD PEDAGÓGICA (CAP) CURSO 20082009 PRÁCTICA 1
CURSO DE APTITUD PEDAGÓGICA (CAP) CURSO 20082009 PRÁCTICA 1 GASTROINTESTINAL • PANCREAS (EXOCRINE) PANCREASEXOCRINE 4001 PROTOCOL FOR THE
GASTROINTESTINAL • PANCREAS (EXOCRINE) PANCREASEXOCRINE 4001 PROTOCOL FOR THEWTDS437R 115 ESTADOS UNIDOS MEDIDAS EN
PARA LOS DIOSES TURCOS MIENTRAS EL CUERPO MUERE POR
 LISTA 4 CONCEITOS IMPORTANTES 1) MOEDA HISTÓRICO E FUNÇÕES
LISTA 4 CONCEITOS IMPORTANTES 1) MOEDA HISTÓRICO E FUNÇÕESASHLEY WHITE DRS BELGRAD SCOTT AND WAKEFIELD DECEMBER 3
 ZAŁĄCZNIK NR 6 DO SPECYFIKACJI ISTOTNYCH WARUNKÓW ZAMÓWIENIA NA
ZAŁĄCZNIK NR 6 DO SPECYFIKACJI ISTOTNYCH WARUNKÓW ZAMÓWIENIA NA Recent%20Judgments%20Bulletin%2024%202017
Recent%20Judgments%20Bulletin%2024%202017TO BE PUBLISHED IN THE GAZETTE OF PAKISTAN EXTRA
 AMST 302 PSCI 335 MARK REINHARDT FALL 2009
AMST 302 PSCI 335 MARK REINHARDT FALL 2009ZAŁĄCZNIK NR 1 DO OGŁOSZENIA SZCZEGÓŁOWY OPIS PRZEDMIOTU ZAMÓWIENIA
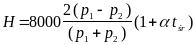 POMIAR CIŚNIENIA ATMOSFERYCZNEGO CIŚNIENIE ATMOSFERYCZNE ĆWICZENIE OBEJMUJE DEFINICJE
POMIAR CIŚNIENIA ATMOSFERYCZNEGO CIŚNIENIE ATMOSFERYCZNE ĆWICZENIE OBEJMUJE DEFINICJEATTACHMENT 10 [NOTIFICATION TO RESUME PERFORMANCE OF CONTRACTS DIRECTED
 PRÄSIDIALDEPARTEMENT DES KANTONS BASELSTADT STAATSARCHIV SEITE 3 BESTELLFORMULAR FÜR
PRÄSIDIALDEPARTEMENT DES KANTONS BASELSTADT STAATSARCHIV SEITE 3 BESTELLFORMULAR FÜRКВАЛИФИКАЦИЯ ДОГОВОРА НА ОСУЩЕСТВЛЕНИЕ ФУНКЦИЙ ЗАКАЗЧИКАЗАСТРОЙЩИКА В СООТВЕТСТВИИ С
 SUPER INTENDENCIA DE SOCIEDADES CÓDIGO GEPR001 SISTEMA GESTIÓN INTEGRADO
SUPER INTENDENCIA DE SOCIEDADES CÓDIGO GEPR001 SISTEMA GESTIÓN INTEGRADO