DISSECTION AND MICROSCOPY OF PLANT VASCULAR TISSUE LEARNING OUTCOMES
2012 HONG KONG HEAD AND NECK SURGERY DISSECTION COURSE3 PLEASE KEEP THIS PORTION FOR YOUR RECORDS DISSECTION
BIOLOGY 2005 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS DISSECTION GUIDE!DO
CATASTROPHIC CASE REPORT CAROTID ARTERY DISSECTIONSTROKE AFTER CENTRAL LINE
DISSECTION AND MICROSCOPY OF PLANT VASCULAR TISSUE LEARNING OUTCOMES
DISSECTION AND SCIENTIFIC DRAWING STUDENT SUPPORT SHEET INTRODUCTION THE


Dissection and microscopy of plant vascular tissue
Learning outcomes
Introduction
These learning outcomes aim to cover subject knowledge requirements for this part of A-level Biology in three specifications (OCR, AQA and Edexcel). You may need to adapt this information for your specification.
This information can be used to produce learning resources, revision materials, quizzes etc.
![]()
Students should be able to:
List the types of cells found in plant stems (*=cell types named in specifications)
*Xylem vessels
*Phloem – sieve tube elements and companion cells
*Sclerenchyma fibres
Parenchyma (make up cortex and pith – which can be mainly hollow)
Collenchyma
Epidermis
Cambium
State the function of xylem vessels, phloem and sclerenchyma fibres in plant stems
Xylem vessels – transport water and mineral ions from the roots to the rest of the plant. They also provide some structural support for the plant.
Phloem – transport sugars from a source to a sink. Photosynthetic cells are sources, cells requiring sugars are sinks (root cells, growing regions). Areas of a plant that store carbohydrates are sinks when they are building up a store but sources when that store is being utilised by the plant.
Sclerenchyma fibres – provide structural support to the plant.
List the two components of phloem and explain why both are needed
Sieve-tube elements – provide the vessels for transport of carbohydrates (relatively hollow tubes provide reduced resistance to flow).
Companion cells – provide the metabolic needs of the sieve-tube elements.
Describe the structure of xylem vessels, phloem and sclerenchyma fibres
Xylem vessels are hollow tubes made up of dead cells. The cells are arranged end on end and the cell walls between each cell are broken down to produce the long hollow tube. The cells have lost all cell contents and have thickened cell walls that have been impregnated with lignin. Xylem vessels also have holes in their walls that connect adjacent vessels.
Phloem are hollow tubes made of up many connected cells (sieve tubes elements). The cell walls between each of the cells are perforated into structures called sieve plates. Each cell contains very little cytoplasm and no nucleus. These cells have cytoplasmic connections with companion cells.
Sclerenchyma fibres are separate cells, pointed at each end, attached together to form fibres. The cells are dead and hollow and have very thickened cell walls that are impregnated with lignin.
Identify xylem vessels, phloem and sclerenchyma fibres in preparations, photos and diagrams of plant stems
A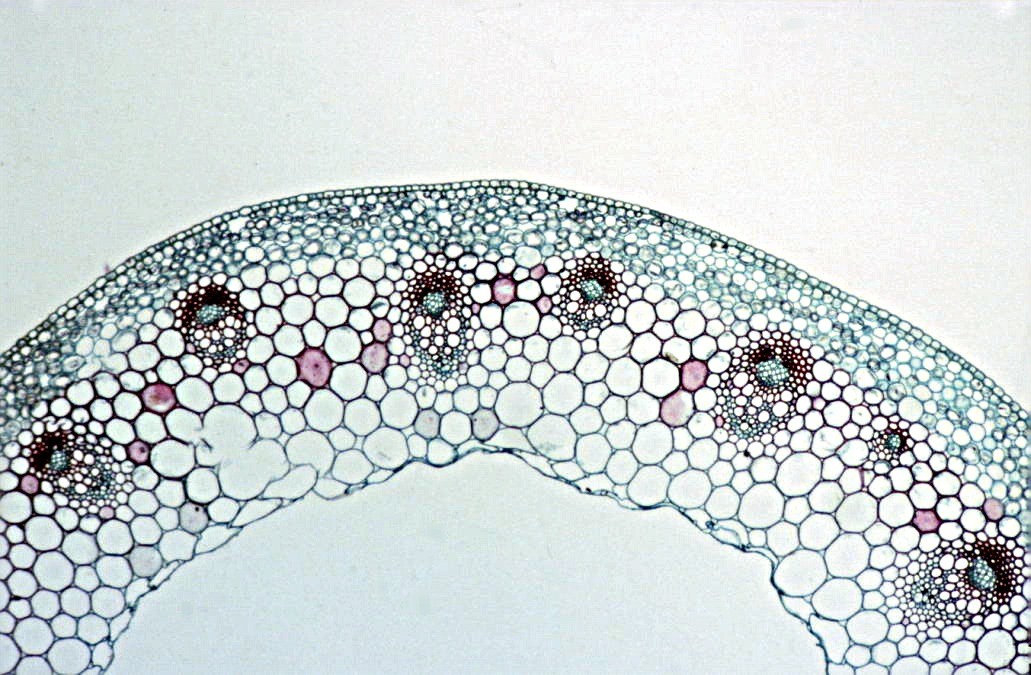

Sclerenchyma fibres


Phloem
Xylem
B
Sclerenchyma fibres
Phloem
Xylem
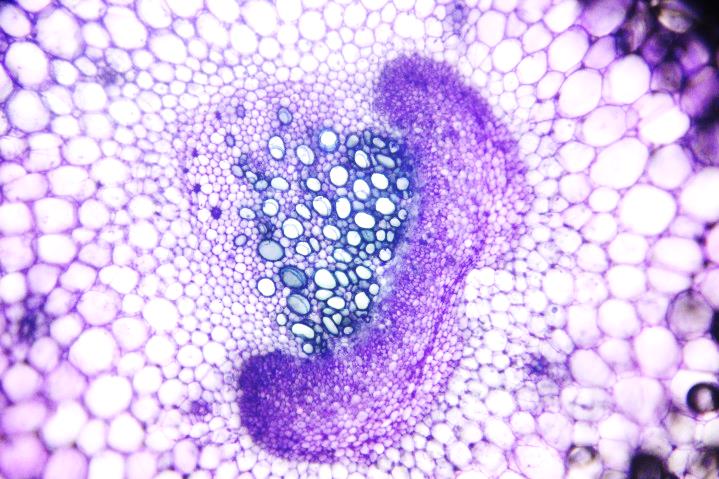
Photomicrographs
A: Transverse section of part of a young stem of
a buttercup (Ranunculus sp.). Image by John Bebbington FRPS
B: Transverse section of a vascular bundle of a
young stem of a buttercup (Ranunculus sp.). Image by John Adds
C: Longitudinal section of xylem vessels from
stem of Sunflower (Helianthus annuus). Image by Leighton Dann
C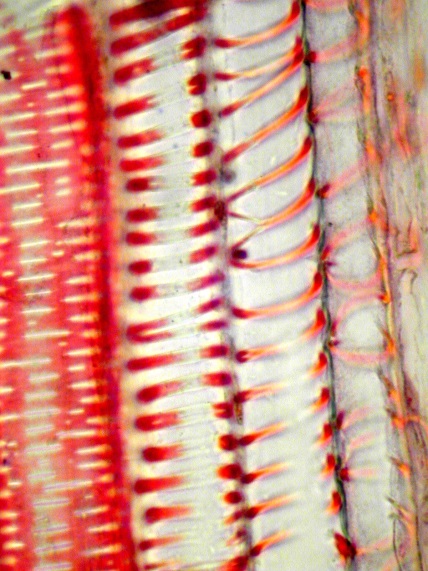
Xylem
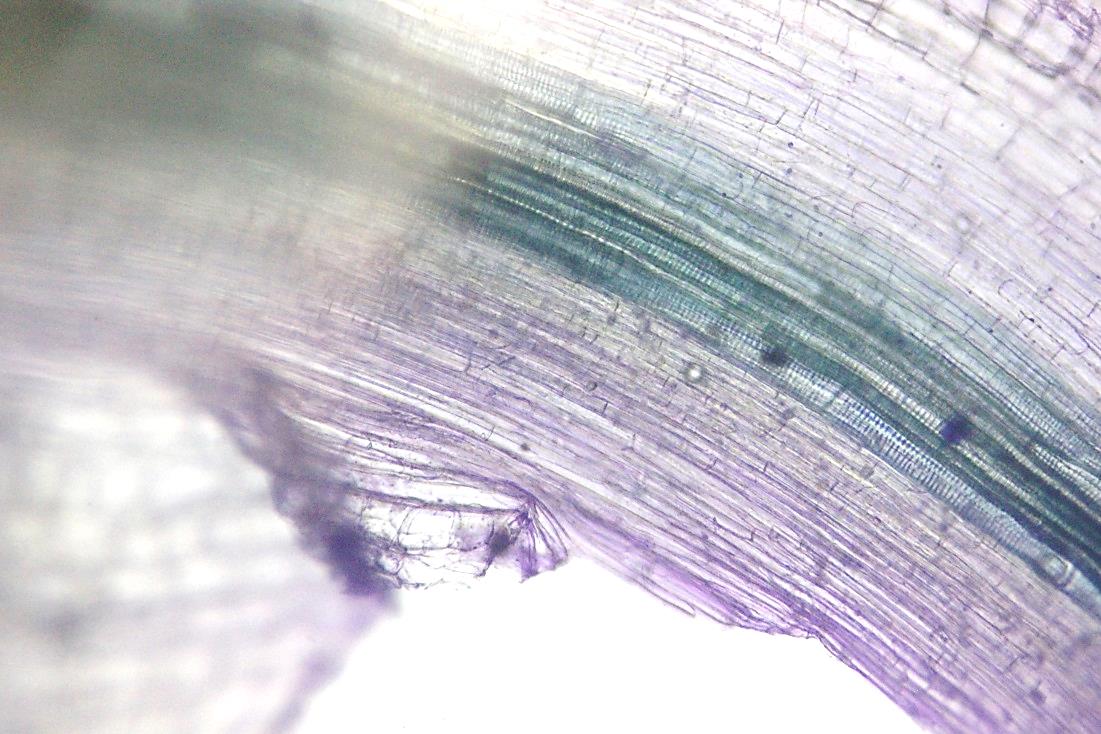
A and B: Preparations of transverse sections through celery stalks
[petioles] (Apium graveolens var dulce)
C and D: Preparations of longitudinal sections through celery stalks
[petioles]
Preparations
of celery petioles (leaf stalks) using this method (Apium
graveolens var
dulce)
Xylem
A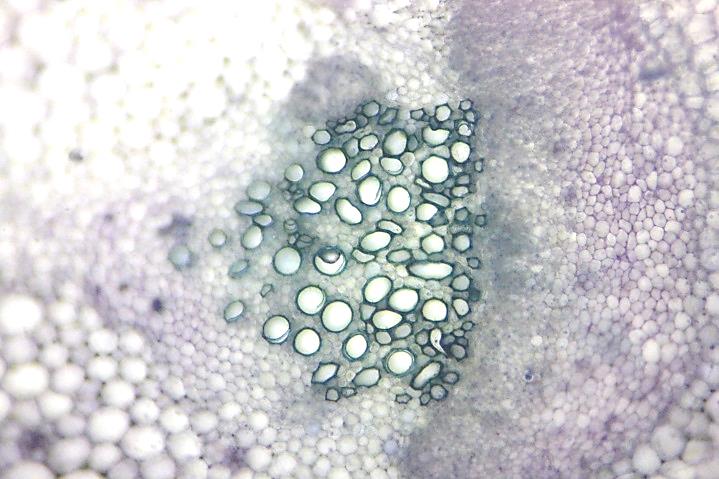
Phloem
B
Xylem
Phloem
C
D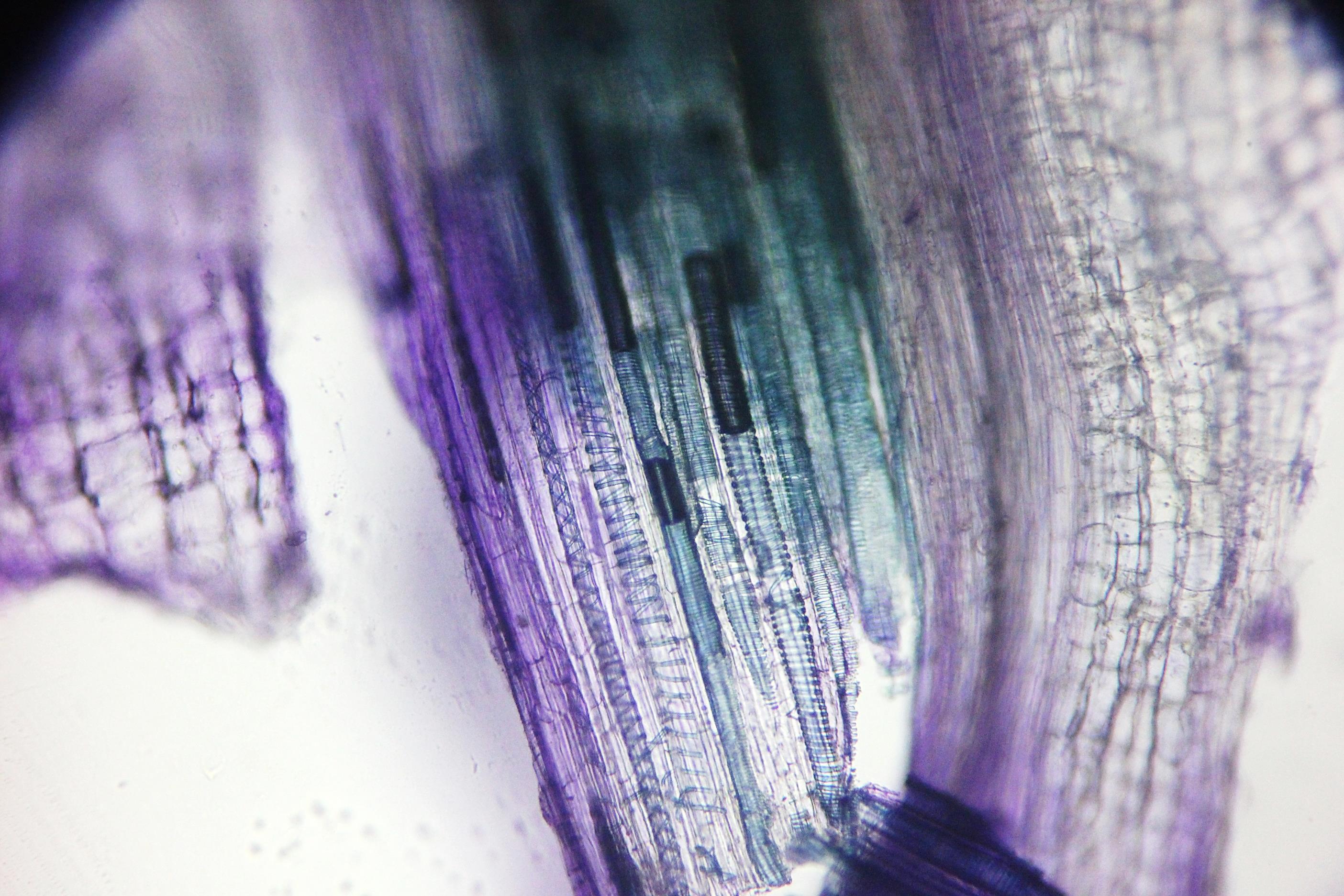
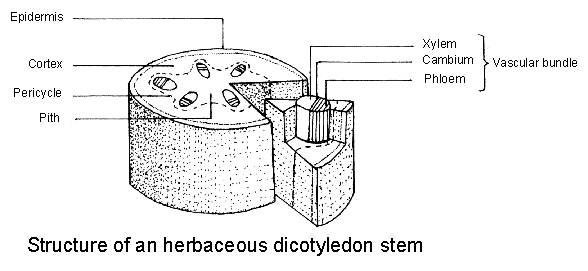
Diagrams
A:
Cross-section through a plant stem (from
http://www.saps.org.uk/secondary/teaching-resources/1324)
B:
Overview of a longitudinal section of a plant stem (image
from www.saps.org.uk/animations)
C:
Detailed longitudinal section of a plant stem (image
from www.saps.org.uk/animations)
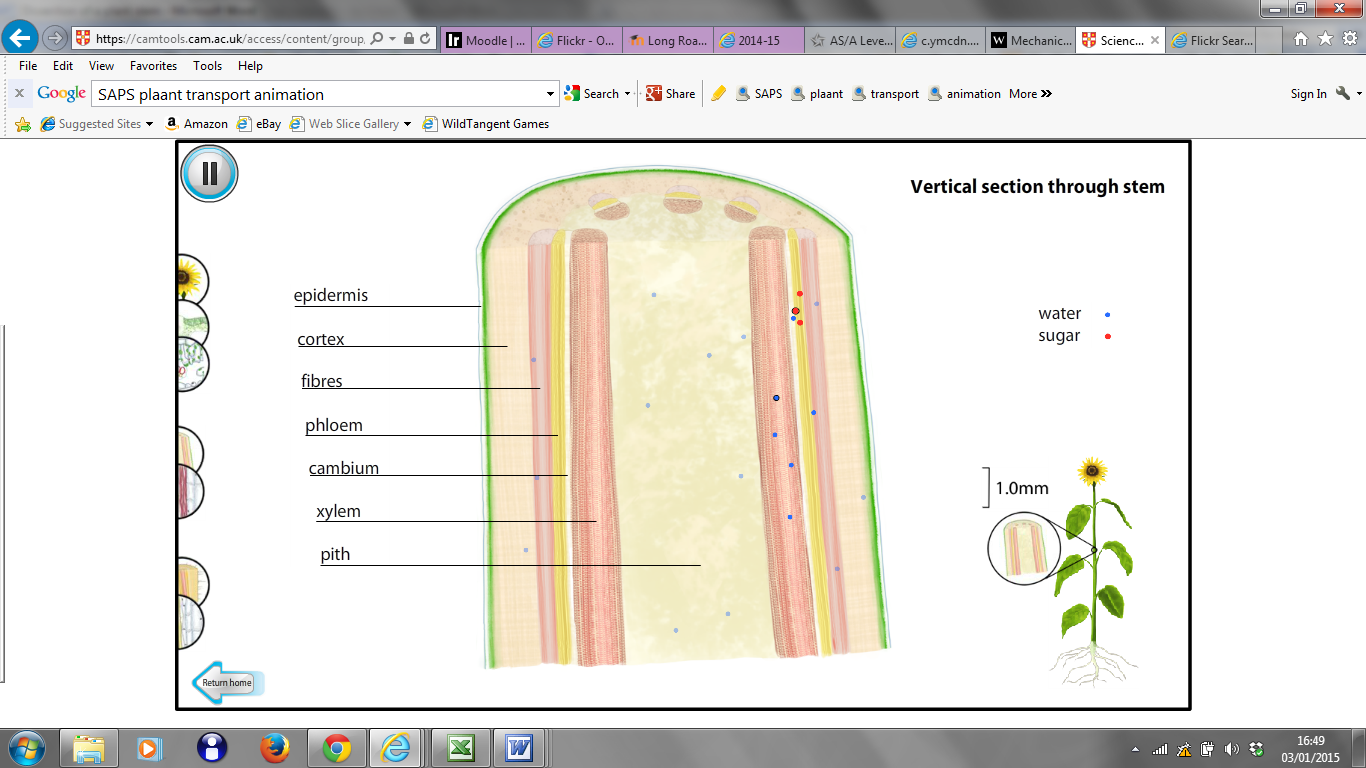
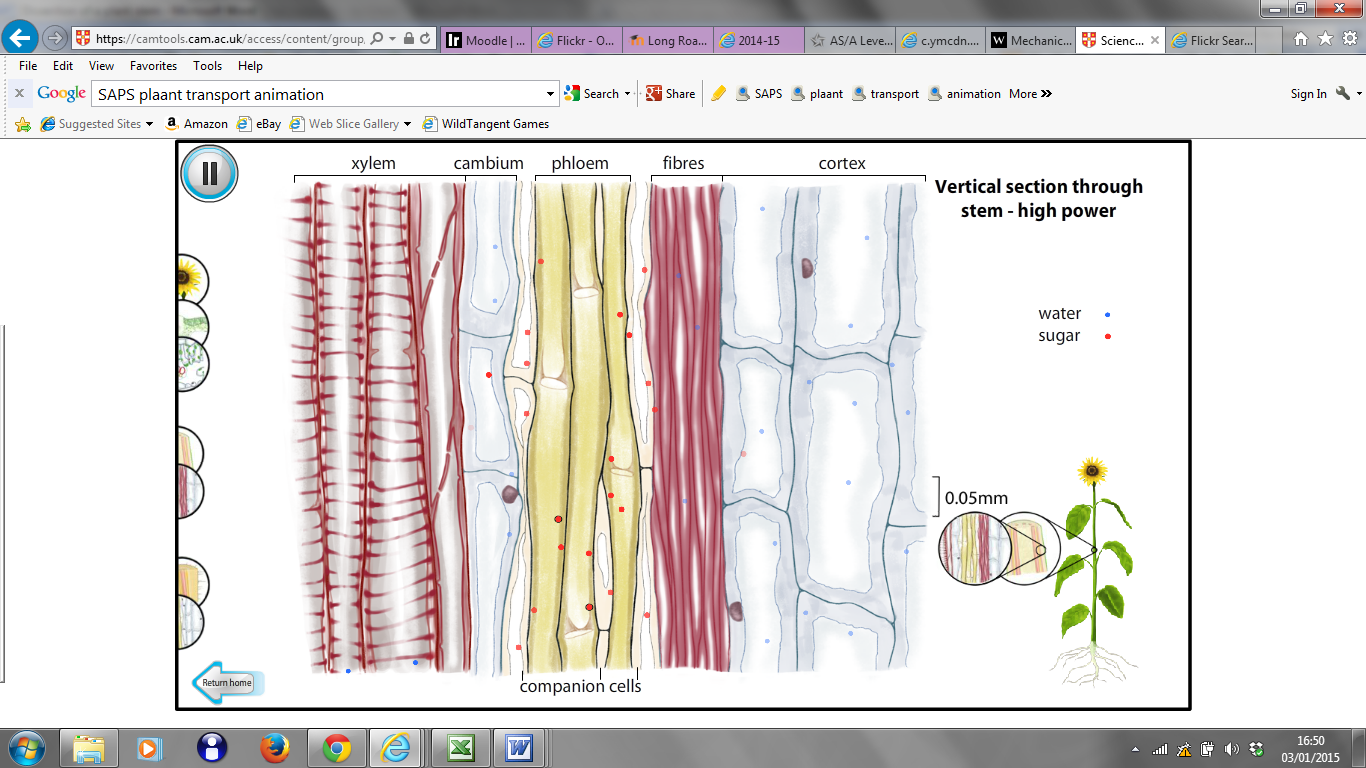
Diagrams
******* get better diagrams – from SAPS?
Describe how the structure of xylem vessels, phloem and sclerenchyma fibres are adapted for their specific function
Xylem
|
Feature |
Function |
|
Dead cells |
Allows the vessels to be hollow |
|
Hollow cells |
Provides a hollow vessel that provides minimum resistance to the flow of water (also reduces weight) |
|
Cells connected end on end |
Provides a continuous vessel for the transport of water |
|
Cell walls between cells broken down |
Reduces the resistance to the flow of water |
|
Thickened cell walls |
Gives the vessels extra strength |
|
Lignified cell walls |
Waterproofs areas of the vessels to reduce water loss and give the vessels extra strength |
|
Holes connecting adjacent tubes |
Allows for horizontal movement of water to maintain vertical movement of water even if there are blockages in the vessels |
Phloem
|
Feature |
Function |
|
Living cells |
Allows the cells to take part in active processes such as the loading of sucrose into the tubes |
|
Cells contain little cytoplasm and no nucleus |
Allow the cells to be relatively hollow |
|
Relatively hollow cells |
Provides a relatively hollow vessel that provides minimum resistance to the flow of dissolved sugars (also reduces weight) |
|
Cells connected end on end |
Provides a continuous vessel for the transport of dissolved sugars |
|
Perforated cell walls between cells (sieve plates) |
Reduces the resistance to the flow of dissolved sugars |
|
Cytoplasmic connections with companion cells |
Allow the companion cells to have metabolic control over the sieve tube elements such as providing the sieve tube element with ATP |
Sclerenchyma
|
Feature |
Function |
|
Dead cells |
Allows the vessels to be hollow |
|
Hollow cells |
Reduces weight (increases strength to weight ratio) |
|
Pointed connected cells |
Provides a large surface area for one cell to be connected to another to give the fibres greater tensile strength |
|
Very thickened cell walls |
Give the vessels extra strength to support the plant |
|
Lignified cell walls |
Give the vessels extra strength to support the plant |
Identify similarities and differences between xylem vessels, phloem and sclerenchyma fibres
|
Feature |
Xylem vessels |
Phloem |
Sclerenchyma fibres |
|
General structure |
Vessels = hollow tubes made of many connected cells |
Vessels = hollow tubes made of many connected cells |
Separate cells joined together to form fibres |
|
Dead / Alive |
Dead cells |
Living cells – sieve tube elements kept alive by connections to companion cells |
Dead cells |
|
Function |
Transport of water and mineral ions Structural support |
Transport of dissolved carbohydrates |
Structural support |
|
Cell wall |
Thickened and possess lignin |
No special modifications (plasmodesmata between sieve tube element and companion cells, also sieve plates at the end of cells) |
Thickened and possess lignin |
|
Cell contents |
Completely hollow – some perforated or slitted end plates of cells remain |
Hollow centre with thin layer of cytoplasm around the edge. Sieve plates at the end of each cell. |
Hollow dead cells |
Science & Plants for Schools: www.saps.org.uk
Dissection
and microscopy of plant vascular tissue – Learning outcomes:
p.
DISSECTION PHYSIOLOGIQUE ET MODÉLISATION DE L’INTERACTION GÉNOTYPE X ENVIRONNEMENT
LAB 14 EYE AND EAR EYEDISSECTION PART I EYE
NAME ALTERNATIVE TROUT DISSECTION PRELAB DO BEFORE VIEWING DISSECTION!!!
Tags: dissection and, www.saps.org.uk dissection, dissection, tissue, vascular, microscopy, outcomes, learning, plant
- MOCIÓ PER A UN DESENVOLUPAMENT RURAL SOSTENIBLE INTEGRAL I
- 7ENTREVISTA MODELO PARA CONTADORES 1 NOMBRE 2 PROFESIÓN 3
- ABGEORDNETENHAUS BERLIN – 15 WAHLPERIODE DRUCKSACHE 15 1422 G
- JAMONES EL CASTELLAR JAELKA JANVIER 2012 1 JAMÓN
- STV 4444 EUROPEISK REGIONALISME OG MULTILEVEL GOVERNANCE FORELESINGSPLAN OG
- LAKE MISSAUKEE COUNTY PARK RATES AND FEES FOR 2021
- 0 0 WORKS SAMPLE BIDDING DOCUMENTS UNDER JAPANESE ODA
- SAVING SALVATION THE AMAZING EVOLUTION OF GRACE BY STEPHEN
- MARKTGEMEINDE ATZENBRUGG 3452 ATZENBRUGG WACHAUER STRASSE 5 BEZIRK TULLN
- GUÍA DE FORMULACIÓN DE EMPRESAS RECTANGLE 18 GUÍA
- ROTC CLASS A UNIFORM A CLASS A UNIFORM CONSISTS
- SAFRA XINGU FUNDO DE INVESTIMENTO EM COTAS DE FUNDOS
- LGAP CONTRACT 16001 REQUEST FOR QUOTATION SPECIFICATION REQUEST FOR
- FONDO DE CONTRIBUCIONES VOLUNTARIAS PARA LOS PUEBLOS INDÍGENAS CONVOCATORIA
- UNA EXPERIENCIA INOLVIDABLE A VECES TENEMOS MIEDO A ARRIESGARNOS
- AANVRAAGFORMULIER ERKENNING INZAKE VERPLICHT PEONDERWERP 2019 TRAINING ‘FRAUDE’ DIT
- EFFECTIVENESS AND SAFETY OF DIRECT ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS IN PATIENTS
- NORSK FORUM FOR KVALITET I HELSETJENESTEN (NFKH) 25 ORDINÆRE
- DISASTER AND EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT ETHICS EAM4043 INSTRUCTOR GEORGE
- SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS RAMADANI ET AL 2015 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES TABLE
- NFN NORSK NETTVERK FOR NÆRINGSEIENDOM NORWEGIAN REAL ESTATE
- CITY OF WAYNE FRAME3 VERSION 20210722 FRAME4 FRAME5 PAYMENT
- ORACIONES HAZME IR MÁS DESPACIO SEÑOR ACOMPASA EL LATIR
- ESTADÍSTICA I – PRÁCTICA 1 POWERPLUSWATERMARKOBJECT3 PRÁCTICA 2 ESTADÍSTICA
- TÜRKİYE PSİKİYATRİ DERNEĞİ BİLİMSEL ÇALIŞMA BİRİMLERİ YÖNERGESİ AMAÇ MADDE
- SLUTTRAPPORTERING KUNNSKAPSSTATUS FOR IAAVTALENS DELMÅL 2 REKRUTTERE OG BEHOLDE
- MOSQUITO ERADICATION ACT OF JUL 10 1935 PL 641
- LITERATURA POSMODERNA FONDO TEMAS Y TÉCNICAS COMUNES DIFERENTES PERSPECTIVAS
- SEZNAM SLOVENSKE IN EVROPSKE ZAKONODAJE SLOVENSKA ZAKONODAJA ZAKONI
- ITALY (UPDATE 28 JAN 06) OP 2 BIOLOGICAL
ÅRSPLAN I ENGELSK FORDYPNING – KRÅKERØY UNGDOMSSKOLE 10TRINN LÆRER
 5 (TEXTO DE APROBACION FINAL POR LA CAMARA) (26
5 (TEXTO DE APROBACION FINAL POR LA CAMARA) (26 D ENOMINACIÓN DEL PUESTO BIBLIOTECARIO DE CIRCULACIÓN OBJETIVOS
D ENOMINACIÓN DEL PUESTO BIBLIOTECARIO DE CIRCULACIÓN OBJETIVOSLEVEL 2 UNIT 17 AZ EGYES UNITOK FELDOLGOZÁSÁNAK AJÁNLOTT
 DE LA REALIDAD DE LA PLURICULTURALIDAD A LA UTOPÍA
DE LA REALIDAD DE LA PLURICULTURALIDAD A LA UTOPÍA ENTREPRISE COLLECTIVE LES INFORMATIONS FINANCIÈRES DES TROIS DERNIERS EXERCICES
ENTREPRISE COLLECTIVE LES INFORMATIONS FINANCIÈRES DES TROIS DERNIERS EXERCICESSAMMANFATTNING VATTEN SAMT VÄRME OCH KYLA ALLT LEVANDE
5 ZAMAWIAJĄCY NAJWYŻSZA IZBA KONTROLI WARSZAWA UL FILTROWA 57
 NOMBRE DE LA CARRERA MEMORIAL JOSE ANTONIO PEREZ ORGANIZADOR
NOMBRE DE LA CARRERA MEMORIAL JOSE ANTONIO PEREZ ORGANIZADOR DOCTORADO EN BIOMEDICINA Y FARMACIA TESIS MENCIÓN DE DOCTOR
DOCTORADO EN BIOMEDICINA Y FARMACIA TESIS MENCIÓN DE DOCTORRCEX11 RCEX11 DECISIÓN CONJUNTA ADOPTADA POR LA CONFERENCIA DE
POROZUMIENIE ZAWARTE W DNIU POMIĘDZY UNIWERSYTETEM WROCŁAWSKIM WE
RESOLUCION Nº 5457 DEL 27 DE AGOSTO DE 1999
MODELCONTRACT SPONSORING VAN EEN VERENIGING ORGANISATIE DE ONDERGETEKENDEN
 TEHNO SHOP DOO CESTA NA BOČ 1 3250 ROGAŠKA
TEHNO SHOP DOO CESTA NA BOČ 1 3250 ROGAŠKALEY 12981 ENCARGADOS DE CASAS DE RENTA Y PROPIEDAD
CALENDRIER DES EXAMENS DU 1ER SEMESTRE 20182019 (SESSION PRINCIPALE)
MODELO DE AVAL PARA LA SUSPENSIÓN DEL PROCEDIMIENTO RECAUDATORIO
 SINONIMOAK LANDU JOSE NAZARETHEKOAK MUNDUKO ERITZI PUBLIKOARI IA BI
SINONIMOAK LANDU JOSE NAZARETHEKOAK MUNDUKO ERITZI PUBLIKOARI IA BI AVISO DE INTENCIÓN PARA PEDIR LA LIBERACIÓN DE FONDOS
AVISO DE INTENCIÓN PARA PEDIR LA LIBERACIÓN DE FONDOS